How much are average utility bills? This question lies at the heart of this comprehensive analysis, which delves into the intricacies of utility costs, exploring the factors that influence them, examining the various types of utility bills, and providing valuable insights into managing and reducing these expenses.
From the impact of location and energy consumption habits to the role of household size and appliances, this exploration unravels the complexities of utility bills, empowering readers with a thorough understanding of their components and how they are calculated.
Factors Affecting Utility Bill Costs: How Much Are Average Utility Bills
Utility bill costs can vary significantly depending on several factors, including location, energy consumption habits, household size, and the types of appliances used.
Average utility bills vary widely depending on location, household size, and consumption habits. For instance, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, the average monthly electricity bill in the United States is around $117. However, this figure can be significantly higher or lower in different regions.
It is worth considering whether investing in software like Norton Utilities Ultimate can help optimize device performance and potentially reduce utility costs. By streamlining system processes and addressing inefficiencies, such software may contribute to overall energy savings, thereby impacting average utility bills.
Location
The location of a residence can have a significant impact on utility bills. Factors such as climate, local energy sources, and government regulations can all affect the cost of utilities. For example, homes in colder climates typically have higher heating bills, while those in warmer climates may have higher cooling bills.
Additionally, areas with access to renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, may have lower electricity costs.
Energy Consumption Habits
The energy consumption habits of a household can also have a major impact on utility bills. Simple changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room or unplugging electronics when not in use, can help to reduce energy consumption and lower bills.
Additionally, using energy-efficient appliances and taking advantage of natural light can further reduce energy usage.
Household Size and Appliances
The size of a household and the types of appliances used can also affect utility bill costs. Larger households typically have higher energy consumption due to increased lighting, heating, and cooling needs. Additionally, appliances that consume a lot of energy, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, and dishwashers, can significantly increase utility bills.
Types of Utility Bills
Utility bills are invoices that detail the charges for essential services such as electricity, gas, water, and trash removal. These bills vary in format and structure depending on the utility provider and the specific services being billed. Understanding the different types of utility bills and their components is crucial for managing household expenses and ensuring timely payments.
Electricity Bills
- Base charge:A fixed fee that covers the cost of maintaining the electrical infrastructure, regardless of usage.
- Usage fees:Variable charges based on the amount of electricity consumed, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
- Demand charges:Additional fees for high peak usage, which can incentivize customers to reduce consumption during peak hours.
- Taxes and surcharges:Government-imposed charges and fees added to the bill.
Gas Bills
- Base charge:Similar to electricity bills, a fixed fee for maintaining the gas distribution system.
- Usage fees:Variable charges based on the volume of gas consumed, typically measured in therms or cubic feet.
- Delivery charges:Fees for transporting gas from the supplier to the customer’s property.
- Taxes and surcharges:As with electricity bills, additional charges may apply.
Water Bills
- Base charge:A fixed fee for access to the water supply system, regardless of usage.
- Usage fees:Variable charges based on the volume of water consumed, typically measured in gallons.
- Sewer charges:Fees for treating and disposing of wastewater.
- Taxes and surcharges:Applicable government charges and fees.
Trash Removal Bills
- Base charge:A fixed fee for the regular collection and disposal of household waste.
- Volume-based charges:Additional fees for exceeding a certain volume of waste.
- Taxes and surcharges:As with other utility bills, additional charges may apply.
Reading and understanding a utility bill requires careful attention to the following:
- Account number:A unique identifier for the customer’s account.
- Billing period:The dates covered by the bill.
- Usage details:A breakdown of the amount of electricity, gas, water, or trash consumed during the billing period.
- Charges:A detailed list of all fees and charges, including base charges, usage fees, and taxes.
- Payment due date:The date by which payment is expected.
Average Utility Bill Costs by Region
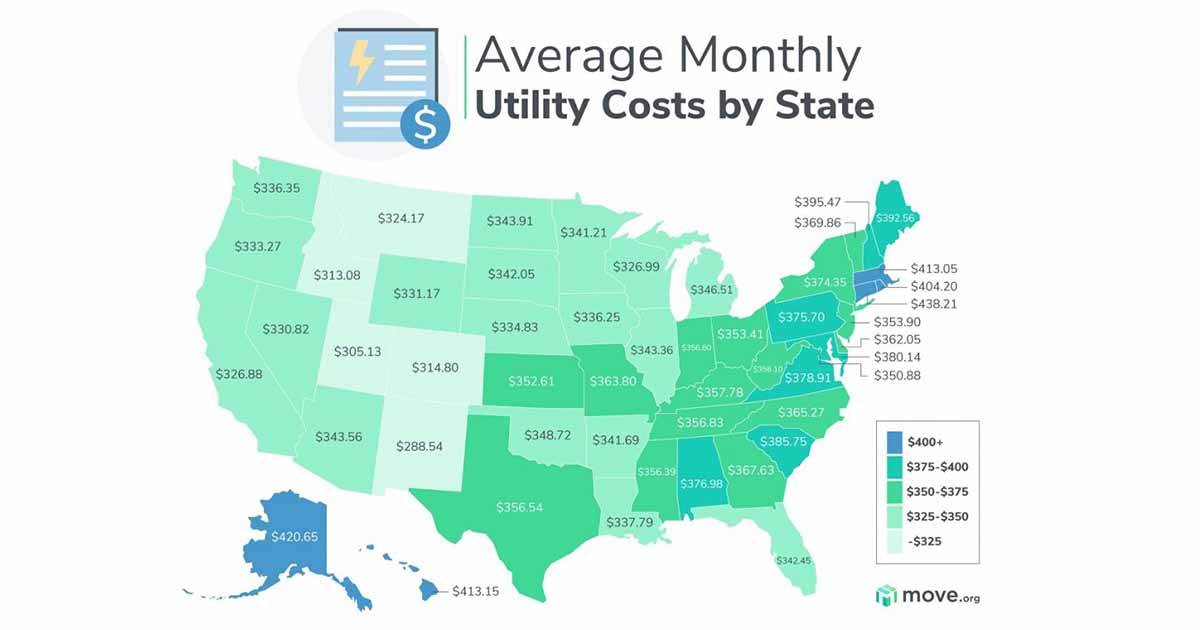
The average utility bill costs vary significantly across different regions in the United States. This variation is primarily due to factors such as climate, population density, and the availability of local energy sources.
The following table shows the average monthly utility bills for different regions in the United States, including data for major metropolitan areas within each region.
Average Utility Bill Costs by Region
| Region | Average Monthly Utility Bill | Major Metropolitan Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | $150 | New York City, Boston, Philadelphia |
| Midwest | $120 | Chicago, Detroit, Minneapolis |
| South | $100 | Atlanta, Houston, Dallas |
| West | $140 | Los Angeles, San Francisco, Seattle |
Seasonal Variations in Utility Bills
Seasonal changes significantly impact utility consumption, particularly for heating and cooling costs. During winter months, households consume more energy for heating, leading to higher utility bills. Conversely, in summer months, air conditioning usage increases, resulting in higher electricity consumption and utility costs.
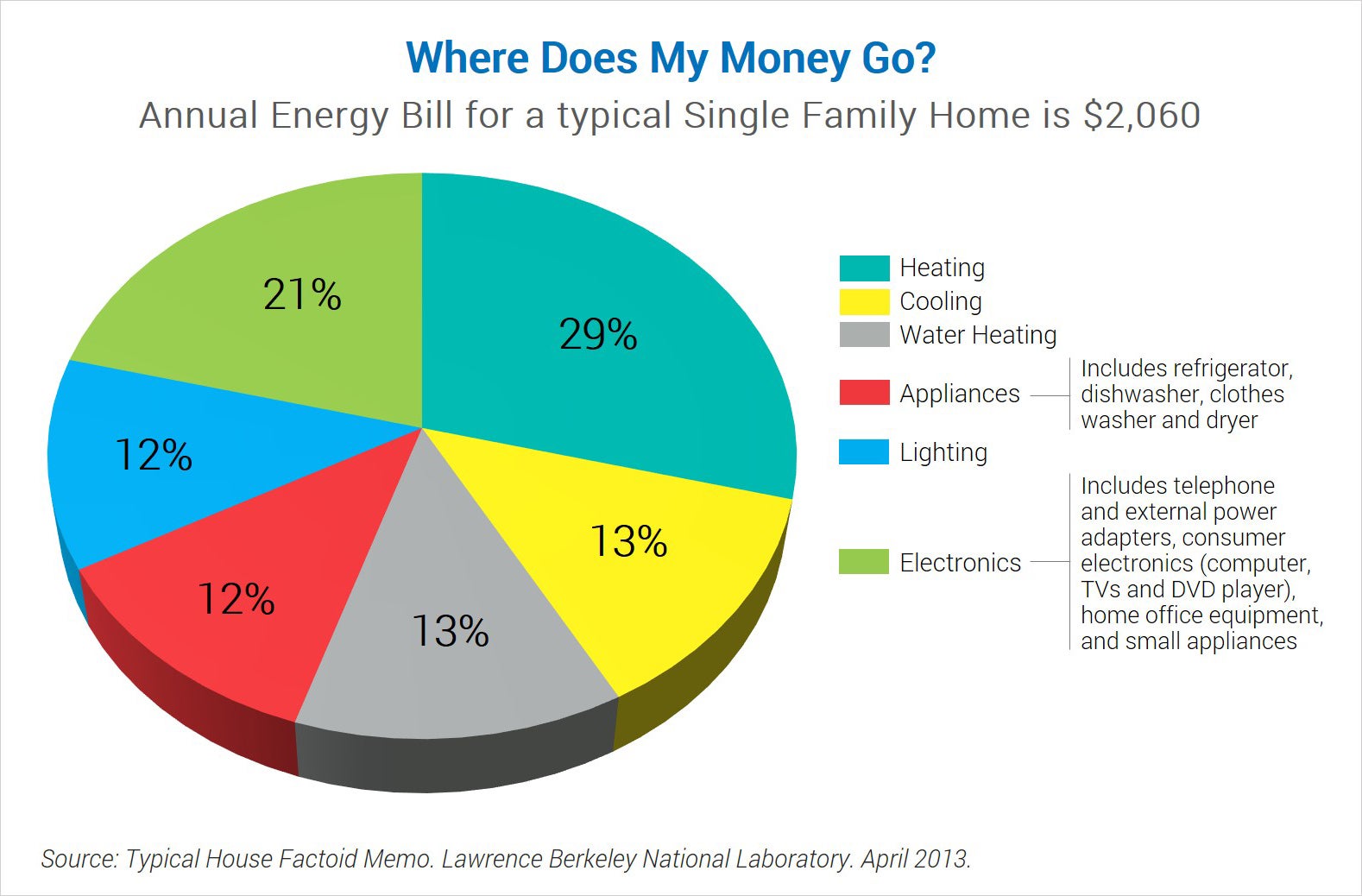
Heating and Cooling Costs
Heating and cooling account for a substantial portion of utility bills, especially in regions with extreme temperatures. In colder climates, heating systems such as furnaces or heat pumps operate more frequently during winter, consuming significant amounts of energy. In warmer climates, air conditioners work overtime during summer to maintain comfortable indoor temperatures, resulting in higher electricity usage.
Monthly Utility Bills by Season
The following table shows the average monthly utility bills for a typical household in different seasons:| Season | Average Monthly Utility Bill ||—|—|| Winter | $150-$250 || Spring | $100-$150 || Summer | $150-$200 || Fall | $100-$150 |
Seasonal Consumption Graph
The graph below illustrates the relationship between seasonal changes and utility consumption. It shows that utility consumption peaks during winter and summer months when heating and cooling needs are highest.[Insert graph here showing seasonal variations in utility consumption]
Summary
Seasonal variations have a significant impact on utility bills, with heating and cooling costs fluctuating throughout the year. Households in colder climates experience higher utility bills during winter due to increased heating needs, while those in warmer climates face higher bills during summer due to air conditioning usage.
Understanding these seasonal variations can help consumers budget for utility expenses and take steps to reduce consumption during peak months.
Energy-Efficient Practices
Implementing energy-efficient practices can significantly reduce utility bills. These practices involve adopting techniques and using appliances that consume less energy, leading to lower utility costs and a reduced environmental impact.
One of the most effective ways to reduce energy consumption is by utilizing energy-efficient appliances. These appliances, such as refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines, are designed to operate with minimal energy usage. By replacing older, less efficient appliances with newer, energy-efficient models, households can significantly reduce their energy consumption and utility bills.
Energy-Efficient Lighting
Another important aspect of energy-efficient practices is the use of energy-efficient lighting. Traditional incandescent light bulbs consume a substantial amount of energy, while energy-efficient alternatives such as compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) and light-emitting diodes (LEDs) consume significantly less energy while providing comparable or even better illumination.
Government Assistance Programs
The government offers a range of assistance programs to help low-income households manage their utility bills. These programs can provide financial assistance, energy efficiency upgrades, and other support services.
To be eligible for these programs, households must meet certain income and other criteria. The application process typically involves submitting an application form and providing proof of income and other documentation.
Programs
| Program | Eligibility Requirements | Application Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) | Income at or below 150% of the federal poverty level | Contact local community action agencies or state energy offices |
| Weatherization Assistance Program (WAP) | Income at or below 200% of the federal poverty level | Contact local community action agencies or state energy offices |
| State Energy Assistance Programs (SEAPs) | Eligibility varies by state | Contact local community action agencies or state energy offices |
The application process for these programs typically involves submitting an application form and providing proof of income and other documentation. Households that are approved for assistance may receive financial assistance, energy efficiency upgrades, or other support services.
Participating in these programs can help low-income households save money on their utility bills and improve their overall quality of life.
For more information on these programs, contact local community action agencies or state energy offices.
Smart Home Technology
Smart home technology plays a pivotal role in managing utility consumption by optimizing energy usage through intelligent devices and automation.Smart thermostats, for instance, learn occupants’ temperature preferences and adjust heating and cooling systems accordingly. They can be programmed to lower temperatures when the home is unoccupied or during off-peak hours, reducing energy consumption.
Other smart devices, such as smart plugs and lighting systems, allow users to remotely control and monitor energy usage, enabling them to identify areas where consumption can be further reduced.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats leverage algorithms and sensors to analyze usage patterns and optimize temperature settings. They can be integrated with other smart devices, such as motion sensors, to detect occupancy and adjust temperatures accordingly. Additionally, smart thermostats provide real-time energy consumption data, allowing users to track their usage and identify opportunities for further savings.
Renewable Energy Options
Harnessing renewable energy sources offers a sustainable and cost-effective approach to reducing utility bills. These sources, such as solar and wind power, generate electricity without relying on finite fossil fuels, resulting in significant savings over time.
Various types of renewable energy systems are available for residential and commercial use:
Solar Energy Systems
- Solar photovoltaic (PV) panels:Convert sunlight directly into electricity.
- Solar thermal collectors:Use sunlight to heat water or air.
Wind Energy Systems
- Wind turbines:Generate electricity from the kinetic energy of the wind.
Geothermal Energy Systems
- Geothermal heat pumps:Use the earth’s natural heat to warm or cool buildings.
Hydroelectric Power Systems
- Micro-hydro turbines:Generate electricity from flowing water sources.
Biomass Energy Systems
- Wood-burning stoves:Use wood pellets or logs to heat homes.
Negotiating Utility Bills
Negotiating lower utility bills can help households and businesses save money on their monthly expenses. It involves contacting service providers and requesting a reduction in rates or fees. To negotiate effectively, it’s important to be prepared and informed about the market rates and available options.
Comparing rates and shopping around for the best deals is essential. This can be done by contacting different service providers and comparing their rates and terms of service. It’s also important to consider any additional fees or charges that may apply.
Tips for Negotiating Lower Utility Bills
- Gather information:Before contacting the service provider, research and compare rates from different providers. This will give you a strong negotiating position.
- Be polite and respectful:When negotiating, it’s important to maintain a positive and professional demeanor. Being rude or demanding is unlikely to yield favorable results.
- Explain your financial situation:If you’re experiencing financial hardship, explain your situation to the service provider. They may be willing to work with you on a payment plan or provide a discount.
- Ask for discounts:Many service providers offer discounts for senior citizens, low-income households, or customers who sign up for automatic payments or paperless billing.
- Consider a payment plan:If you’re struggling to pay your utility bills on time, ask the service provider about payment plans. This can help you spread out your payments over a longer period.
Understanding Utility Bill Statements
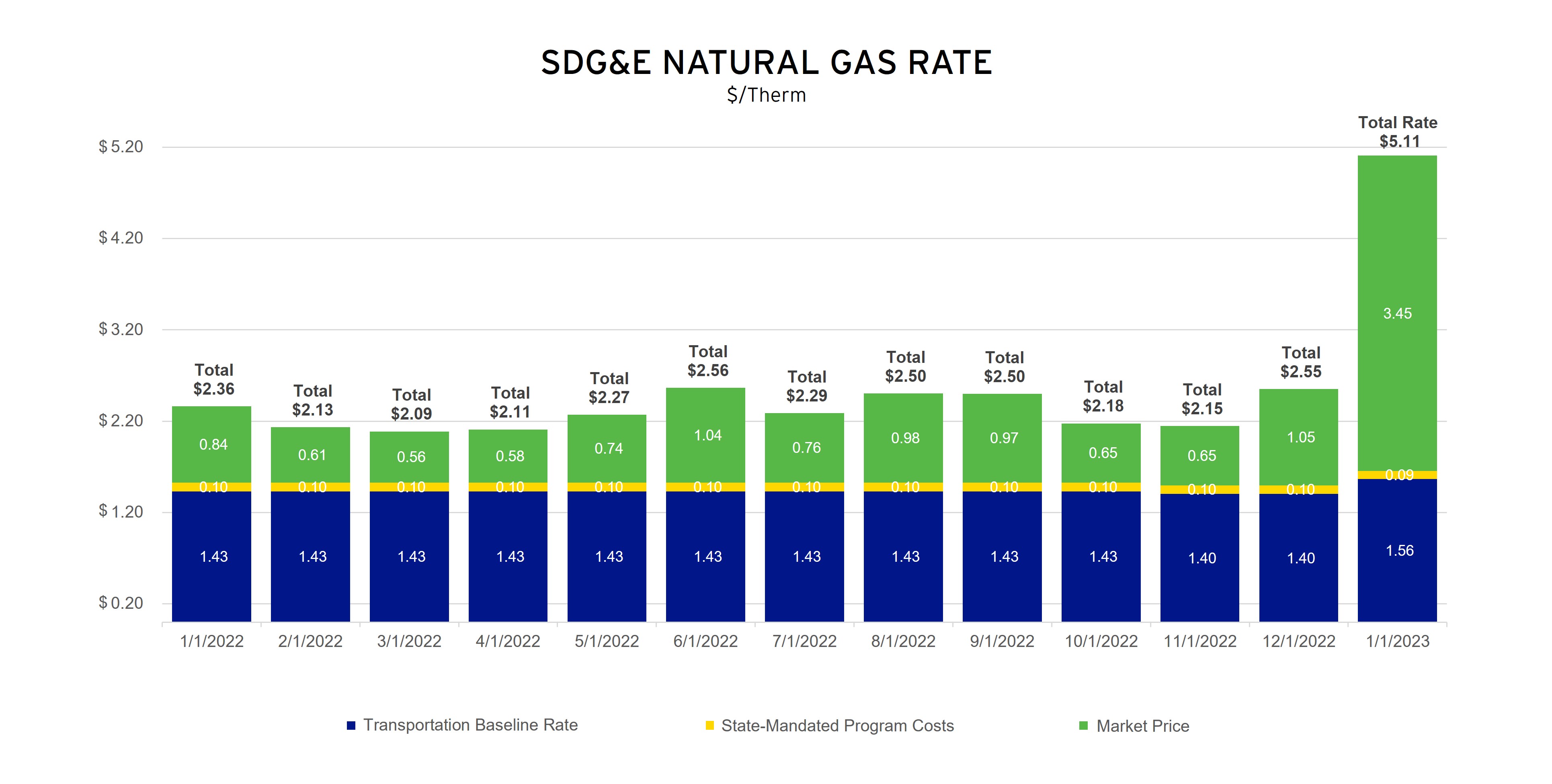
Understanding utility bill statements is crucial for managing household finances effectively. These statements provide detailed information about energy consumption, charges, and payment details.
Sample Utility Bill Statement
[Insert a sample utility bill statement image or link] Key Sections of a Utility Bill Statement:
The average utility bill in the United States is around $110 per month, but this can vary depending on the size of your home, the number of people living in your home, and the climate in your area. If you’re looking for a way to reduce your utility bills, one thing you can do is to get a body composition measurement using calipers.
Which body composition measurement utilizes calipers can help you determine your body fat percentage, which can be helpful for setting weight loss goals and tracking your progress. By understanding your body composition, you can make changes to your diet and exercise routine to help you reach your goals and potentially reduce your utility bills by reducing your energy consumption.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Usage Charges | Charges for electricity, gas, water, etc., based on consumption. |
| Taxes and Fees | Government-imposed taxes and fees related to energy usage. |
| Payment Due Date | Date by which the bill must be paid to avoid late fees. |
| Payment Methods | Available methods for paying the bill, such as online, by mail, or in person. |
| Customer Service Contact Information | Contact details for assistance with billing inquiries or issues. |
Importance of Understanding Utility Bill Statements
Understanding utility bill statements is essential for several reasons:
Identifying and Calculating Usage Charges
Accurately calculating usage charges helps monitor energy consumption and identify potential savings opportunities.
Understanding Taxes and Fees
Knowing the types and amounts of taxes and fees charged ensures proper budgeting and financial planning.
Knowing When to Contact Customer Service
Promptly addressing billing issues or discrepancies requires understanding the bill’s contents.
Bill Pay Options
Customers have various options for paying their utility bills, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these options can help customers choose the best method for their individual needs and circumstances.
The following table compares the different bill payment methods available:
| Payment Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Online Bill Pay |
|
|
| Mail-In Payments |
|
|
| Phone Payments |
|
|
| In-Person Payments |
|
|
| Auto Pay |
|
|
The best payment method depends on the individual’s circumstances and preferences. Customers should consider factors such as convenience, security, cost, and reliability when choosing a payment method.
Best Practices
- For those who prioritize convenience and security, online bill pay or auto pay are recommended.
- For those who prefer traditional methods or have limited internet access, mail-in payments may be suitable.
- For those who value immediate processing, in-person payments can be an option.
- Customers should carefully review the terms and conditions of each payment method to ensure they understand any fees or restrictions.
- It is important to choose a payment method that aligns with the individual’s financial situation and lifestyle.
Utility Bill Scams
Utility bill scams are fraudulent attempts to obtain money or personal information from unsuspecting customers. Scammers may use various tactics, including phone calls, emails, or even in-person visits, to trick customers into paying fake bills or providing sensitive information.
It is crucial for customers to be aware of these scams and take steps to protect themselves.
Identifying Utility Bill Scams, How much are average utility bills
- Unexpected contact:Scammers may contact customers out of the blue, claiming to be from the utility company and demanding immediate payment.
- High-pressure tactics:Scammers often use aggressive language and threaten to disconnect service if payment is not made immediately.
- Request for personal information:Scammers may ask for personal information, such as Social Security numbers or bank account details, under the guise of verifying the customer’s account.
- Fake invoices:Scammers may send fake invoices that look similar to legitimate utility bills but contain fraudulent information.
Avoiding Utility Bill Scams
- Never give out personal information over the phone or email:Legitimate utility companies will not ask for personal information over the phone or email.
- Be wary of unsolicited contact:If you receive an unexpected call or email from someone claiming to be from your utility company, do not provide any information.
- Verify the caller’s identity:If you are unsure whether the caller is legitimate, hang up and call the utility company directly using the phone number on your bill.
- Inspect invoices carefully:If you receive an invoice that looks suspicious, compare it to your previous bills and contact your utility company to verify its authenticity.
- Report suspicious activity:If you suspect you have been the victim of a utility bill scam, report it to your utility company and the Federal Trade Commission (FTC).
Resources for Utility Assistance
Individuals and families facing financial hardship may qualify for assistance with their utility bills. Numerous organizations and government programs provide support to help cover these essential expenses.
The following table lists some key resources that offer utility assistance:
Organizations Providing Utility Assistance
| Organization | Contact Information | Type of Assistance | Eligibility Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Energy Assistance Referral (NEAR) | 1-866-674-6327 | Financial aid, energy efficiency programs | Income-based |
| Salvation Army | 1-800-725-2769 | Financial aid, energy bill payment assistance | Income-based, need-based |
| United Way | 1-800-427-4626 | Financial aid, energy efficiency programs | Income-based, need-based |
| National Fuel Funds Network | 1-800-444-3863 | Financial aid, energy efficiency programs | Income-based, need-based |
| LIHEAP (Low Income Home Energy Assistance Program) | Varies by state | Financial aid, energy bill payment assistance | Income-based |
Future Trends in Utility Billing
The utility industry is undergoing a transformation driven by technological advancements and changing consumer demands. Emerging trends in utility billing, such as time-of-use pricing, smart grid technology, and blockchain applications, are reshaping the way utilities operate and interact with their customers.
Time-of-Use Pricing
Time-of-use pricing is a billing mechanism that charges consumers different rates for electricity usage depending on the time of day. This pricing structure aims to shift energy consumption away from peak hours when demand is high and costs are typically higher.
By incentivizing consumers to use energy during off-peak hours, time-of-use pricing can help utilities balance grid load, reduce peak demand, and potentially lower overall energy costs.
However, implementing time-of-use pricing requires careful planning and consumer education. Consumers need to understand how their usage patterns affect their bills and adjust their energy consumption accordingly. Additionally, utilities need to ensure that time-of-use pricing does not lead to increased costs for low-income or vulnerable consumers.
Smart Grid Technology
Smart grid technology refers to the integration of advanced sensors, communication networks, and data analytics into the electricity grid. This technology enables utilities to monitor and control the grid in real-time, improving efficiency, reducing outages, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources.
Smart grid technology can provide numerous benefits to consumers, including improved reliability, reduced energy costs, and access to new energy management services. For example, smart meters can provide consumers with real-time information about their energy usage, allowing them to identify areas where they can save energy and reduce their bills.
Blockchain Applications
Blockchain technology is a distributed ledger system that can be used to create secure and transparent records of transactions. In the utility industry, blockchain can be used to improve billing processes, reduce fraud, and enable peer-to-peer energy trading.
Blockchain-based billing systems can enhance transparency and accountability, as all transactions are recorded on a public ledger that can be audited by consumers. Additionally, blockchain can help reduce fraud by preventing unauthorized changes to billing records. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, allowing consumers to sell excess solar energy back to the grid or directly to other consumers.
General Inquiries
What factors influence utility bill costs?
Location, energy consumption habits, household size, and appliances all play a role in determining utility bill costs.
What are the common types of utility bills?
Electricity, gas, water, and trash are the most common types of utility bills.
How can I reduce my utility bills?
Energy-efficient practices, such as using energy-efficient appliances and lighting, can help reduce utility bills.




