How to calculate utilization – In the realm of business and operations, calculating utilization is a critical aspect of optimizing resource efficiency. It empowers organizations to assess the extent to which their assets, capacity, and labor are being utilized, enabling data-driven decision-making and improved performance.
This academic presentation will delve into the intricacies of utilization calculation, exploring various methods, types, and factors that influence utilization rates. We will also examine advanced techniques for utilization analysis and discuss ethical considerations in utilization management.
Introduction to Utilization Calculation
Utilization is a key metric used to assess the efficiency and productivity of resources, assets, or systems. It measures the extent to which a resource is being used compared to its full potential or capacity. Understanding utilization is crucial in various fields, including business, engineering, and manufacturing.
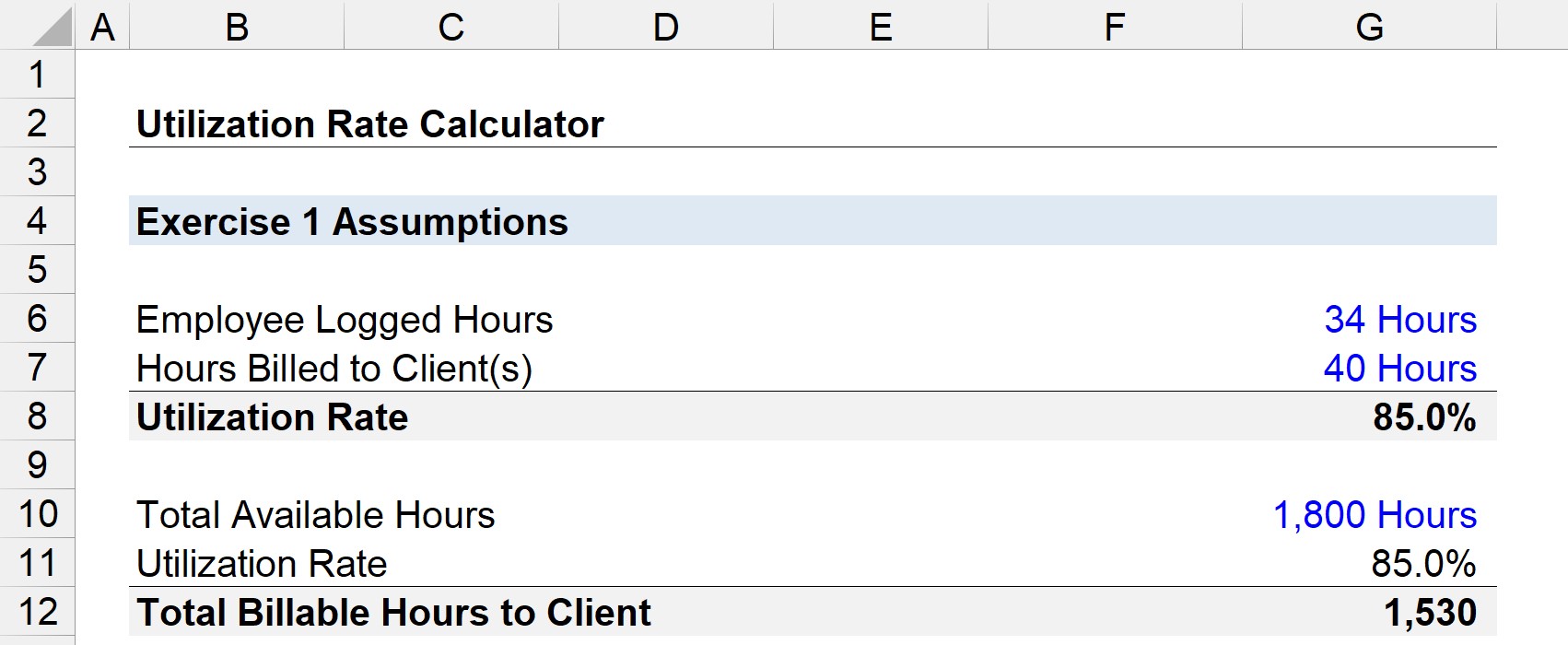
In business, utilization is commonly used to measure the efficiency of employees, equipment, and facilities. For example, employee utilization calculates the percentage of time an employee is engaged in productive work. High utilization indicates efficient resource allocation, while low utilization may suggest underutilized resources or inefficiencies.
Examples of Industries Where Utilization is Crucial
- Manufacturing:Utilization is essential for optimizing production processes, minimizing downtime, and ensuring efficient use of machinery and equipment.
- Healthcare:Utilization is used to assess the efficiency of medical equipment, staff workload, and hospital beds, ensuring optimal patient care and resource allocation.
- Transportation:Utilization is crucial for managing fleet operations, optimizing vehicle usage, and reducing idle time, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
- Energy:Utilization is used to assess the efficiency of energy generation and distribution systems, ensuring optimal utilization of resources and minimizing waste.
Methods for Calculating Utilization
Utilization is a measure of how efficiently a resource is being used. It can be calculated using a variety of methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Average Utilization
Average utilization is the simplest method to calculate utilization. It is calculated by dividing the total amount of time that a resource is used by the total amount of time that the resource is available.
Formula:“`Average Utilization = Total Time Used / Total Time Available“` Steps:
- Determine the total amount of time that the resource was used.
- Determine the total amount of time that the resource was available.
- Divide the total time used by the total time available.
Example:A machine is used for a total of 8 hours per day. The machine is available for use for a total of 10 hours per day. The average utilization of the machine is 8 hours / 10 hours = 0.8, or 80%.
Peak Utilization
Peak utilization is the maximum amount of time that a resource is used during a given period.
Formula:“`Peak Utilization = Maximum Time Used / Total Time Available“` Steps:
- Determine the maximum amount of time that the resource was used during the given period.
- Determine the total amount of time that the resource was available during the given period.
- Divide the maximum time used by the total time available.
Example:A machine is used for a maximum of 10 hours on a given day. The machine is available for use for a total of 10 hours per day. The peak utilization of the machine on that day is 10 hours / 10 hours = 1, or 100%.
Minimum Utilization
Minimum utilization is the minimum amount of time that a resource is used during a given period.
To calculate utilization, you need to know the total number of units in a property and the number of units that are currently occupied. You can then divide the number of occupied units by the total number of units to get the utilization rate.
Do you pay utilities in an apartment ? The answer to this question depends on the terms of your lease. Some leases include the cost of utilities in the rent, while others require tenants to pay for utilities separately. If you are responsible for paying utilities, you should factor the cost of utilities into your budget when calculating the total cost of renting an apartment.
Formula:“`Minimum Utilization = Minimum Time Used / Total Time Available“` Steps:
- Determine the minimum amount of time that the resource was used during the given period.
- Determine the total amount of time that the resource was available during the given period.
- Divide the minimum time used by the total time available.
Example:A machine is used for a minimum of 6 hours on a given day. The machine is available for use for a total of 10 hours per day. The minimum utilization of the machine on that day is 6 hours / 10 hours = 0.6, or 60%.
Other Methods
There are a number of other methods that can be used to calculate utilization, including:
- Weighted average utilization
- Capacity utilization
- Throughput utilization
The best method for calculating utilization will depend on the specific application.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Each method for calculating utilization has its own advantages and disadvantages.
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Average Utilization | Simple to calculate | Can be misleading if the resource is not used evenly throughout the period |
| Peak Utilization | Shows the maximum amount of time that the resource is used | Can be misleading if the resource is not used at peak capacity for a significant period of time |
| Minimum Utilization | Shows the minimum amount of time that the resource is used | Can be misleading if the resource is not used at minimum capacity for a significant period of time |
Interpreting the Results
The results of utilization calculations can be used to improve the efficiency of a resource.
- If the utilization is too low, then the resource is not being used efficiently and could be used more effectively.
- If the utilization is too high, then the resource is being overused and could be damaged or fail.
By understanding the utilization of a resource, it is possible to make informed decisions about how to use it more efficiently.
Examples, How to calculate utilization
Utilization calculations are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Capacity planning
- Resource allocation
- Performance management
By understanding the utilization of a resource, it is possible to improve the efficiency of the resource and the overall performance of the system.
Types of Utilization
Utilization is a measure of how efficiently a resource is being used. There are many different types of utilization, each with its own specific metrics.
Some of the most common types of utilization include:
- Asset utilizationmeasures how efficiently a physical asset, such as a machine or building, is being used.
- Capacity utilizationmeasures how efficiently a production process is being used.
- Labor utilizationmeasures how efficiently a workforce is being used.
Asset Utilization
Asset utilization is measured by dividing the actual output of an asset by its potential output.
Asset Utilization = Actual Output / Potential Output
For example, if a machine is capable of producing 100 units per hour, but is only actually producing 80 units per hour, then its asset utilization is 80%.
Capacity Utilization
Capacity utilization is measured by dividing the actual output of a production process by its potential output.
Capacity Utilization = Actual Output / Potential Output
For example, if a factory is capable of producing 1,000 units per day, but is only actually producing 800 units per day, then its capacity utilization is 80%.
Labor Utilization
Labor utilization is measured by dividing the actual hours worked by employees by the total number of hours available for work.
Labor Utilization = Actual Hours Worked / Total Hours Available
For example, if a workforce is available to work 40 hours per week, but is only actually working 32 hours per week, then its labor utilization is 80%.
Factors Affecting Utilization
Utilization rates can be influenced by a range of internal and external factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective utilization management and optimization.
Internal Factors
Internal factors originate within the organization and can significantly impact utilization levels.
- Organizational Culture and Leadership:The organization’s culture and leadership style can shape employee motivation, productivity, and work-life balance, which can affect utilization.
- Workforce Planning and Scheduling:Effective workforce planning and scheduling can ensure that the right number of staff is available at the right time, optimizing utilization.
- Resource Allocation and Availability:Availability and allocation of resources, such as equipment, materials, and space, can impact utilization rates.
- Technology and Infrastructure:Technology and infrastructure can enhance efficiency and productivity, leading to improved utilization.
- Process and Workflow Design:Well-designed processes and workflows can streamline operations, reduce waste, and increase utilization.
External Factors
External factors are beyond the organization’s direct control but can influence utilization rates.
- Market Demand and Competition:Market demand and competition can affect utilization levels, especially in industries with seasonal or cyclical patterns.
- Economic Conditions:Economic conditions, such as recessions or economic growth, can impact utilization rates as organizations adjust to changing market conditions.
- Regulatory and Policy Changes:Regulatory and policy changes can impact utilization rates, such as changes in labor laws or environmental regulations.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements can automate tasks, increase efficiency, and improve utilization rates.
- Social and Cultural Trends:Social and cultural trends, such as changes in work patterns or societal norms, can influence utilization rates.
Key Stakeholders Involved in Utilization Management
Effective utilization management requires collaboration among key stakeholders, including:
- Management and leadership
- Human resources
- Operations and production
- Finance and budgeting
- Employees and their representatives
Best Practices for Optimizing Utilization Rates
Organizations can optimize utilization rates by implementing best practices such as:
- Regularly monitoring and analyzing utilization data
- Identifying and addressing bottlenecks and inefficiencies
- Implementing process improvements and workflow automation
- Providing training and development opportunities to employees
- Fostering a culture of continuous improvement and optimization
Benchmarking Utilization: How To Calculate Utilization
Benchmarking utilization is a critical practice that allows organizations to compare their performance against industry standards or competitors. It helps identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and enhance overall efficiency.
Conducting utilization benchmarking involves the following steps:
- Identify relevant metrics and industry standards:
- Determine key utilization metrics that align with the organization’s objectives.
- Gather industry data or competitor information to establish benchmarks.
- Collect data and calculate utilization:
- Track and record relevant data points to calculate utilization metrics.
- Use standardized methods and formulas to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Compare results and analyze gaps:
- Compare the organization’s utilization metrics to benchmarks.
- Identify areas where utilization falls short or exceeds expectations.
- Develop improvement plans:
- Based on the analysis, develop targeted strategies to improve utilization.
- Implement process improvements, resource optimization, or capacity planning initiatives.
- Monitor progress and make adjustments:
- Regularly track progress and compare results to benchmarks.
- Make necessary adjustments to improvement plans based on ongoing monitoring.
Key Metrics for Utilization Benchmarking
Common utilization metrics used for benchmarking include:
| Metric | Definition |
|---|---|
| Asset Utilization | Measures the percentage of time an asset is in use. |
| Capacity Utilization | Indicates the percentage of a system’s or resource’s maximum capacity that is being used. |
| Employee Utilization | Assesses the percentage of time employees are engaged in productive work. |
| Equipment Utilization | Determines the percentage of time equipment is in operation. |
| Space Utilization | Measures the percentage of space in a facility that is being occupied. |
Case Study: Successful Utilization Benchmarking
Company A, a manufacturing firm, implemented a comprehensive utilization benchmarking program. By comparing its equipment utilization rates to industry benchmarks, they identified significant underutilization in certain areas. This led to the implementation of lean manufacturing principles, improved production scheduling, and optimized equipment maintenance, resulting in a 15% increase in equipment utilization and a 10% reduction in production costs.
Additional Resources for Utilization Benchmarking
- American Productivity & Quality Center (APQC): https://www.apqc.org/
- Institute of Industrial Engineers (IIE): https://www.iienet.org/
- Manufacturing Execution Systems Association (MESA): https://www.mesa.org/
– Improving Utilization
![]()
Improving utilization rates involves implementing strategies and techniques to increase the effective use of resources, such as equipment, facilities, or personnel. By optimizing utilization, organizations can enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency.
Successful case studies have demonstrated the positive impact of utilization optimization. For example, a manufacturing company implemented a lean manufacturing system, resulting in a 20% increase in machine utilization and a 15% reduction in production costs.
Strategies for Improving Utilization
There are several key strategies for improving utilization rates:
- Capacity Planning:Accurately forecasting demand and aligning resources accordingly to avoid underutilization or overcapacity.
- Scheduling Optimization:Using advanced scheduling algorithms to allocate resources efficiently, minimize idle time, and maximize throughput.
- Process Improvement:Streamlining processes to reduce bottlenecks, eliminate waste, and increase the effective use of resources.
- Employee Training:Providing training to employees to enhance their skills and capabilities, enabling them to operate equipment and perform tasks more efficiently.
- Preventive Maintenance:Regularly maintaining equipment and facilities to prevent breakdowns and ensure optimal performance.
Benefits of Improved Utilization
Improving utilization has a direct impact on business outcomes, including:
- Increased Revenue:Higher utilization rates lead to increased production or service delivery, resulting in higher revenue generation.
- Reduced Costs:Optimizing utilization reduces idle time and waste, leading to lower operating costs.
- Improved Efficiency:Enhanced utilization eliminates bottlenecks and streamlines processes, resulting in improved operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction:Improved utilization enables organizations to meet customer demand more effectively, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
Best Practices for Optimizing Utilization
Organizations can follow these best practices to optimize utilization:
- Establish Utilization Metrics:Define clear utilization metrics and track them regularly to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Use Data Analysis:Analyze utilization data to identify trends, patterns, and potential bottlenecks.
- Implement Continuous Improvement:Regularly review and refine utilization strategies to ensure ongoing optimization.
- Foster a Culture of Efficiency:Encourage employees to embrace efficient practices and actively participate in utilization improvement initiatives.
Data Collection and Analysis

Data collection is a crucial step in calculating utilization accurately. It provides the necessary information to assess the extent to which resources are being used and identify areas for improvement.
The type of data required depends on the specific utilization calculation being performed. Generally, it includes:
- Resource availability:This includes the total amount of resources available, such as equipment, staff, or space.
- Resource usage:This refers to the amount of resources actually used during a specific period.
- Time period:The time period over which the utilization is being calculated.
Data can be collected through various methods, including:
- Direct observation:Observing and recording the usage of resources in real-time.
- Logs and records:Using existing logs or records that document resource usage.
- Surveys and questionnaires:Collecting data from users or stakeholders about their resource usage.
- Sensor data:Using sensors to collect data on resource usage, such as equipment uptime or occupancy levels.
Once the data is collected, it needs to be analyzed to calculate utilization. This typically involves using statistical methods to determine the percentage of time or capacity that resources are being used.
Technology for Utilization Management
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing utilization management by providing tools and software that automate and streamline the process. These tools assist in collecting, tracking, and analyzing data, enabling healthcare providers to make informed decisions about resource allocation and utilization.
Specific Software and Tools
Numerous software and tools are available to support utilization management. Some notable examples include:
- Utilization Review Software:Automates the review of medical records to ensure appropriate utilization of services, reducing the risk of over-utilization and improving efficiency.
- Data Analytics Platforms:Provide advanced data analysis capabilities, allowing healthcare providers to identify trends, patterns, and outliers in utilization data.
- Predictive Modeling Tools:Utilize machine learning algorithms to predict future utilization patterns, enabling proactive planning and resource allocation.
- Patient Management Systems:Integrate with utilization management systems to provide real-time access to patient data, facilitating timely and informed decision-making.
Case Studies and Examples

Real-world case studies and examples showcase the practical application of utilization calculations in various industries. These examples highlight the challenges, successes, metrics, and impact of utilization on operational efficiency and profitability.
Calculating utilization involves determining the percentage of resources being used by a system. To assess whether Norton Utilities Ultimate is a worthwhile investment, it’s crucial to evaluate its impact on system utilization. Is Norton Utilities Ultimate Worth It ? provides insights into the software’s effects on utilization, enabling informed decision-making regarding its purchase.
Manufacturing Industry
A manufacturing company implemented a utilization tracking system to monitor machine uptime and identify areas for improvement. By analyzing utilization data, they identified bottlenecks in the production process and implemented targeted interventions. As a result, machine utilization increased by 15%, leading to a 10% increase in production output and a reduction in operating costs.
Healthcare Industry
A hospital used utilization calculations to optimize staff scheduling and reduce overtime costs. By tracking nurse and physician utilization, the hospital identified periods of understaffing and overstaffing. Adjustments were made to schedules, resulting in a 20% reduction in overtime pay and improved patient care outcomes.
Transportation Industry
A logistics company employed utilization calculations to maximize the efficiency of its fleet. By monitoring vehicle utilization, they identified underutilized vehicles and optimized routing. This resulted in a 12% increase in fleet utilization, reducing fuel consumption and increasing revenue.
Impact on Operational Efficiency and Profitability
Improved utilization has a direct impact on operational efficiency and profitability. Higher utilization rates lead to increased production output, reduced operating costs, and improved resource allocation. By identifying and addressing underutilized assets, organizations can maximize their efficiency and optimize profitability.
Best Practices for Improving Utilization
- Establish clear utilization targets and metrics.
- Implement data collection and analysis systems to track utilization.
- Identify and address bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Optimize schedules and resource allocation.
- Monitor and benchmark utilization regularly.
Industry-Specific Considerations
Calculating utilization varies across industries due to unique operational characteristics and performance metrics. Here are key considerations and best practices for specific sectors:
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, utilization measures the efficiency of production processes. Key metrics include:
- Equipment Utilization: Percentage of time machines are actively producing goods.
- Labor Utilization: Percentage of time employees are engaged in productive activities.
- Capacity Utilization: Percentage of production capacity being utilized.
Best practices include:
- Regular equipment maintenance to minimize downtime.
- Optimizing production schedules to reduce idle time.
- Training employees to improve productivity and efficiency.
Healthcare
In healthcare, utilization measures the efficiency of medical resources. Key metrics include:
- Bed Occupancy Rate: Percentage of beds occupied by patients.
- Operating Room Utilization: Percentage of time operating rooms are in use.
- Staffing Utilization: Percentage of time healthcare professionals are engaged in patient care.
Best practices include:
- Optimizing patient scheduling to reduce bed vacancies.
- Improving operating room efficiency by reducing setup and turnaround times.
- Managing staffing levels to ensure adequate coverage without overstaffing.
Transportation
In transportation, utilization measures the efficiency of vehicles and infrastructure. Key metrics include:
- Vehicle Utilization: Percentage of time vehicles are in operation.
- Infrastructure Utilization: Percentage of time roads, bridges, and other infrastructure are in use.
- Logistics Efficiency: Percentage of time goods are in transit without delays.
Best practices include:
- Optimizing vehicle routes to minimize empty runs.
- Maintaining infrastructure to prevent breakdowns and delays.
- Improving logistics processes to reduce transit times and inventory holding costs.
Limitations of Utilization Calculations
Utilization calculations, while valuable, have certain limitations that must be acknowledged. These limitations can introduce errors and inaccuracies into the results, potentially affecting decision-making processes.
One significant limitation is the reliance on historical data. Utilization calculations typically use data from past periods to estimate future utilization rates. However, historical data may not always reflect current or future trends. Changes in market conditions, technological advancements, or organizational restructuring can render historical data less relevant.
Data Accuracy and Availability
The accuracy of utilization calculations depends heavily on the quality and availability of data. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading results. For example, if data on equipment downtime or employee absences is not accurately recorded, the utilization rate may be overstated or understated.
Assumptions and Simplifications
Utilization calculations often involve assumptions and simplifications to make the calculations manageable. For instance, it may assume that all resources are equally efficient or that demand is constant. These assumptions may not always hold true in practice, leading to potential inaccuracies.
Mitigating Limitations
To mitigate these limitations, several strategies can be employed:
- Use a combination of historical data and real-time data to improve the accuracy of utilization calculations.
- Regularly review and update historical data to ensure it remains relevant.
- Carefully consider the assumptions and simplifications made in the calculations and assess their potential impact on the results.
- Conduct sensitivity analysis to determine how changes in input parameters affect the utilization rate.
Advanced Techniques for Utilization Analysis
Advanced statistical techniques and models offer deeper insights into utilization patterns by identifying trends, correlations, and anomalies. These techniques include regression analysis, time series analysis, and machine learning algorithms.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis establishes the relationship between a dependent variable (utilization) and one or more independent variables (factors affecting utilization). By fitting a line or curve to the data, regression analysis can predict utilization based on changes in the independent variables.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis examines utilization data over time to identify patterns and trends. It can forecast future utilization based on historical data and seasonal variations. Techniques like ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) and SARIMA (Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) are commonly used.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms, such as decision trees, random forests, and neural networks, can uncover complex relationships and patterns in utilization data. They can classify utilization patterns, predict future utilization, and identify anomalies.
Provide specific examples of how data visualization has been used to improve utilization in healthcare settings.
Data visualization has emerged as a powerful tool for improving utilization in healthcare settings. By translating complex data into visual representations, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into resource allocation, identify areas for optimization, and make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency.
Dashboards and Visualization Tools
Interactive dashboards and visualization tools play a crucial role in tracking key utilization metrics. For instance, bed occupancy dashboards provide real-time visibility into bed availability, allowing hospitals to optimize bed allocation, reduce wait times, and improve patient flow. Similarly, OR utilization dashboards track the usage of operating rooms, enabling surgical teams to identify underutilized time slots and maximize OR efficiency.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Data visualization helps uncover trends and patterns in utilization data. Time-series charts, for example, allow providers to visualize changes in utilization over time, revealing seasonal variations, peak periods, and underutilized resources. By identifying these patterns, healthcare organizations can proactively adjust staffing levels, schedule appointments, and allocate resources to meet fluctuating demand.
Communicating Utilization Results
Data visualization is an effective way to communicate utilization results to stakeholders, including clinicians, administrators, and policymakers. Visual representations make complex data more accessible and understandable, facilitating informed decision-making. Interactive dashboards allow users to drill down into specific metrics, explore different scenarios, and gain a comprehensive understanding of utilization patterns.
Best Practices for Data Visualization
To maximize the effectiveness of data visualization for utilization, certain best practices should be followed:
- Use clear and concise visuals that are easy to interpret.
- Choose the appropriate visualization type based on the data and the intended audience.
- Provide context and annotations to help users understand the data.
li>Enable interactivity and allow users to explore the data.
Case Studies and Examples
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the successful use of data visualization to improve utilization in healthcare settings. For instance, a hospital in the United States implemented a data visualization platform to track bed occupancy and patient flow. The platform identified underutilized beds and enabled the hospital to optimize bed allocation, reducing patient wait times by 20%.
Challenges and Limitations
While data visualization offers significant benefits, it also presents certain challenges and limitations. Data quality and accuracy are crucial, as poor-quality data can lead to misleading visualizations. Additionally, the choice of visualization type and the design of the dashboard can influence the interpretation of the data.
It is important to involve stakeholders in the design process to ensure the visualizations meet their needs.
Future Research and Development
Research and development in the area of data visualization for utilization continue to advance. Future directions include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate data analysis and identify opportunities for improvement. Additionally, the development of standardized metrics and visualization templates will facilitate the comparison of utilization data across different healthcare organizations.
Ethical Considerations in Utilization Management
Utilization management involves collecting and analyzing data on healthcare resource utilization. It is essential to ensure that this data is handled ethically and responsibly, respecting patient privacy and avoiding potential biases.
Best practices for ethical utilization management include:
Data Privacy and Confidentiality
- Adhering to data protection regulations and obtaining informed consent from patients before collecting and using their data.
- Implementing robust data security measures to protect patient information from unauthorized access or misuse.
- Anonymizing or de-identifying data whenever possible to maintain patient confidentiality.
Avoiding Bias and Discrimination
- Using data analysis techniques that minimize bias and ensure fair representation of different patient populations.
- Avoiding using utilization data to make decisions that could discriminate against certain groups of patients based on factors such as race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
- Regularly reviewing and updating utilization management practices to identify and address any potential biases.
Transparency and Accountability
- Providing patients with clear and accessible information about how their data is being used.
- Establishing a process for patients to request access to and correct their utilization data.
- Holding healthcare providers accountable for using utilization data responsibly and ethically.
Question & Answer Hub
What are the key methods for calculating utilization?
Common methods include the ratio of actual output to potential output, time-based utilization, and equivalent units of production.
How can I interpret the results of utilization calculations?
Utilization rates indicate the extent to which resources are being used. High utilization may suggest efficiency, while low utilization may indicate underutilization or inefficiencies.
What are some best practices for optimizing utilization rates?
Best practices include optimizing workforce scheduling, implementing lean manufacturing principles, and investing in technology to enhance resource utilization.


