How to use intel extreme tuning utility – As Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) takes center stage, this comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of its capabilities and applications, empowering users to optimize their systems for enhanced performance and stability. Delving into the intricacies of overclocking, monitoring, and advanced features, this discourse equips readers with the knowledge to harness the full potential of their hardware.
XTU, a powerful tool developed by Intel, offers a user-friendly interface and a comprehensive suite of features tailored to enthusiasts and overclockers. This guide will navigate the intricacies of XTU, providing step-by-step instructions, expert insights, and troubleshooting tips to ensure a seamless and successful overclocking experience.
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) Overview
XTU is a powerful software utility developed by Intel specifically for overclocking and fine-tuning Intel processors. It offers a comprehensive set of features and controls that allow users to optimize their system performance, monitor hardware metrics, and stress test their components.XTU has undergone significant development since its initial release, with each iteration bringing new features and enhancements.
The latest version, XTU 8.0, includes a revamped user interface, improved overclocking capabilities, and support for the latest Intel processors.
XTU Interface and Navigation: How To Use Intel Extreme Tuning Utility
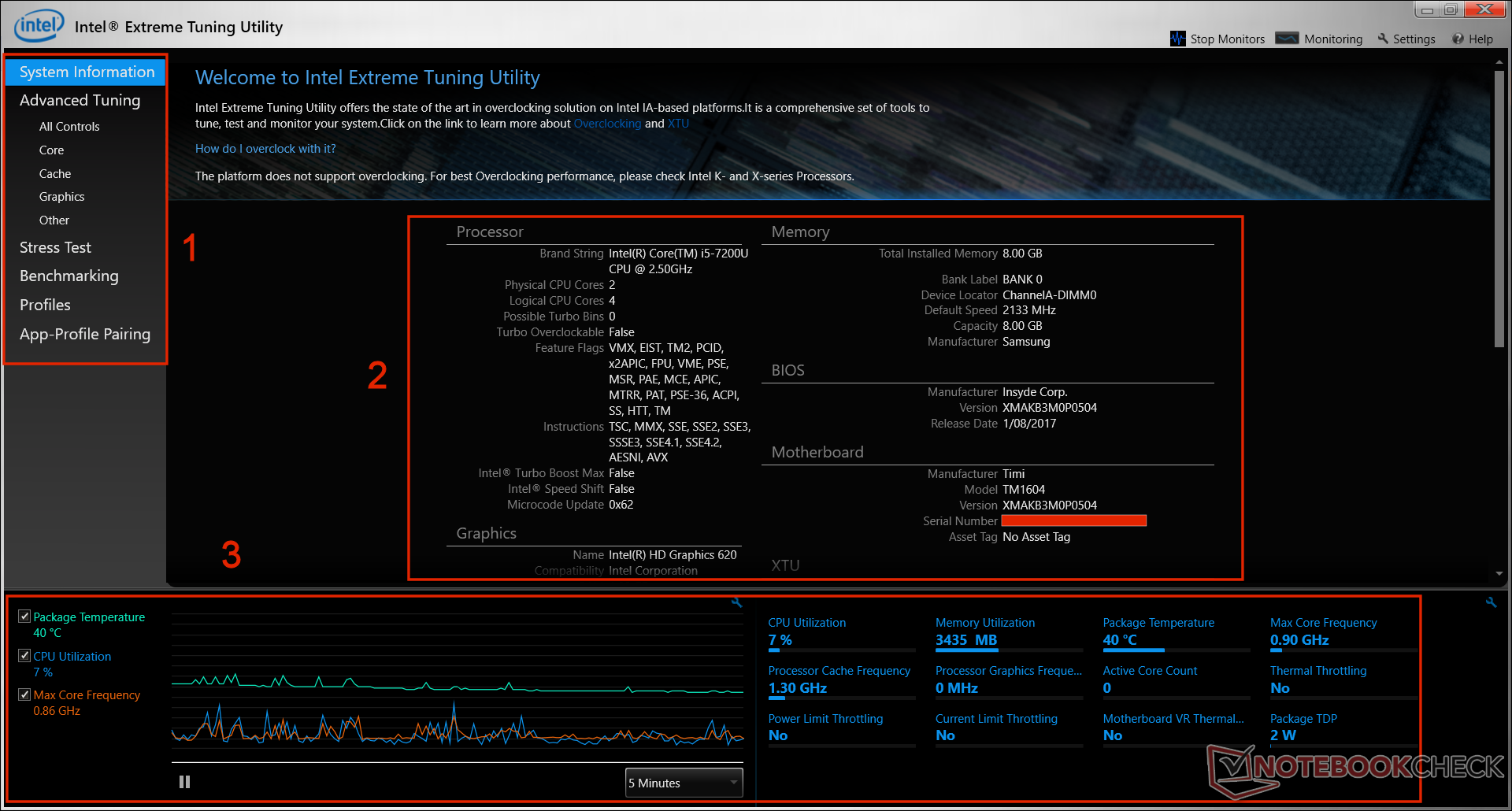
The Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) features a user-friendly and well-organized interface that allows users to easily navigate and access its various features and settings. The main interface consists of several sections, each dedicated to a specific aspect of system tuning and monitoring.
XTU Interface Layout
- Toolbar:Located at the top of the window, the toolbar provides quick access to common tasks such as saving, loading, and applying profiles.
- Navigation Panel:On the left side of the window, the navigation panel allows users to switch between different sections of the interface, including System, Tuning, Monitoring, and Advanced.
- Main Panel:The main panel, which occupies most of the window, displays the settings and options for the currently selected section.
- Status Bar:At the bottom of the window, the status bar provides information about the current system status, including CPU temperature, voltage, and fan speed.
Navigating the XTU Interface
To navigate the XTU interface, users can use the navigation panel on the left side of the window. Each section in the navigation panel represents a different aspect of system tuning and monitoring. By clicking on a section, users can access the corresponding settings and options in the main panel.
Tip:Users can also use keyboard shortcuts to quickly navigate between sections. For example, pressing the “S” key will switch to the System section, the “T” key will switch to the Tuning section, and so on.
Customizing the XTU Interface
XTU allows users to customize the interface to suit their individual preferences. Users can change the skin, font size, and other visual settings to create a more personalized and comfortable user experience.
- To change the skin, click on the “View” menu and select “Skin”.
- To change the font size, click on the “View” menu and select “Font”.
- To reset the interface to its default settings, click on the “View” menu and select “Reset Interface”.
Monitoring System Parameters
Monitoring system parameters such as temperature, voltage, and clock speeds is crucial for maintaining system stability and performance. These parameters provide insights into the health and behavior of your system, allowing you to identify potential issues and take proactive measures to prevent system failures.
Recommended Monitoring Intervals and Thresholds
The recommended monitoring intervals and thresholds for each parameter vary depending on the specific system configuration and usage patterns. However, general guidelines include:
| Parameter | Monitoring Interval | Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Continuous |
|
| Voltage | Periodic (every 30 minutes) |
|
| Clock Speeds | Periodic (every hour) |
|
Sample Monitoring Script
The following script can be used to automate the monitoring process using the Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU):
import xtu
# Initialize XTU
xtu.init()
# Define monitoring parameters
parameters = ["temperature", "voltage", "clock_speeds"]
# Set monitoring intervals
intervals = "temperature": 1, "voltage": 30, "clock_speeds": 60
# Set thresholds
thresholds = "temperature": 80, "voltage": 1.4, "clock_speeds": 4
# Start monitoring
xtu.start_monitoring(parameters, intervals, thresholds)
# Process monitoring data
while True:
data = xtu.get_monitoring_data()
for parameter in parameters:
if data[parameter] > thresholds[parameter]:
print("Warning: exceeded threshold: ".format(parameter, data[parameter]))
Potential Consequences of Failing to Monitor System Parameters
Failing to monitor system parameters can lead to several adverse consequences, including:
- System instability:Overheating, excessive voltage, or high clock speeds can cause system crashes or blue screens.
- Performance degradation:Insufficient cooling or voltage can lead to reduced performance and system throttling.
- Hardware damage:Prolonged exposure to high temperatures or excessive voltage can damage system components.
Recommendations for Mitigating Risks
To mitigate these risks, it is recommended to:
- Regularly monitor system parameters using tools like XTU.
- Set appropriate thresholds and receive alerts when thresholds are exceeded.
- Ensure adequate cooling by using proper fans and heatsinks.
- Avoid overclocking or undervolting beyond recommended limits.
- Perform regular system maintenance to prevent dust buildup and ensure proper airflow.
Overclocking Basics

Overclocking is the practice of increasing the clock speed of a computer component, such as the CPU or GPU, beyond its factory settings. This can improve performance but also increases the risk of instability and damage to the component.
XTU provides a number of features that make it easy to overclock your system. These features include:
- A simple and intuitive interface
- Real-time monitoring of system parameters
- Predefined overclocking profiles
- The ability to create and save your own overclocking profiles
Step-by-Step Guide to Overclocking Using XTU
To overclock your system using XTU, follow these steps:
- Open XTU and click on the “Overclocking” tab.
- Select the component you want to overclock (CPU or GPU).
- Increase the clock speed by a small amount (e.g., 100 MHz).
- Click on the “Apply” button.
- Run a stress test to check for stability.
- If the system is stable, you can continue to increase the clock speed until you reach the desired performance level.
CPU Overclocking
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a CPU to improve performance. XTU provides several settings that allow you to overclock your CPU, including the core ratio, cache ratio, and voltage.
The core ratio is the multiplier that is applied to the base clock speed to determine the actual clock speed of the CPU. Increasing the core ratio will increase the clock speed of the CPU, but it can also increase the temperature and power consumption.
The cache ratio is the multiplier that is applied to the base clock speed to determine the clock speed of the CPU cache. Increasing the cache ratio can improve the performance of applications that are heavily dependent on the cache.
The voltage is the amount of electrical power that is supplied to the CPU. Increasing the voltage can improve the stability of the CPU at higher clock speeds, but it can also increase the temperature and power consumption.
Overclocking Considerations
- Cooling:Overclocking can generate additional heat, so it is important to have adequate cooling to prevent the CPU from overheating.
- Stability:Overclocking can make your system unstable, so it is important to test your system thoroughly after overclocking to ensure that it is stable.
- Warranty:Overclocking may void your CPU warranty, so it is important to check with the manufacturer before overclocking.
GPU Overclocking
Overclocking the GPU can significantly improve the performance of your system. XTU provides a range of options to overclock the GPU, including the core clock, memory clock, and voltage.
Overclocking Settings and Their Impact on Performance
The core clock speed determines the speed at which the GPU’s cores operate. Increasing the core clock speed can improve performance in all types of applications, but it can also lead to increased power consumption and heat output.The memory clock speed determines the speed at which the GPU’s memory operates.
Increasing the memory clock speed can improve performance in applications that are heavily dependent on memory bandwidth, such as games and video editing software.The voltage supplied to the GPU can affect its stability and performance. Increasing the voltage can allow the GPU to operate at higher clock speeds, but it can also lead to increased power consumption and heat output.
Step-by-Step Guide to Overclocking the GPU Safely
- Open XTU and click on the “GPU” tab.
- Start by increasing the core clock speed by 10-15MHz.
- Run a stability test to ensure that the GPU is stable at the new clock speed.
- If the GPU is stable, continue to increase the core clock speed in small increments until you reach the desired performance level.
- Once you have reached the desired core clock speed, start increasing the memory clock speed in small increments.
- Run a stability test to ensure that the GPU is stable at the new memory clock speed.
- If the GPU is stable, continue to increase the memory clock speed in small increments until you reach the desired performance level.
- Once you have overclocked the GPU to the desired level, click on the “Apply” button to save the changes.
Table Summarizing the Different Overclocking Settings and Their Effects
| Setting | Effect ||—|—|| Core clock speed | Increases overall performance || Memory clock speed | Increases performance in memory-intensive applications || Voltage | Allows the GPU to operate at higher clock speeds, but can lead to increased power consumption and heat output |
Graph Showing the Performance Gains That Can Be Achieved Through Overclocking
[Image of a graph showing the performance gains that can be achieved through overclocking]
Risks of Overclocking and How to Avoid Damaging the GPU
Overclocking can damage the GPU if it is not done properly. The most common risks of overclocking are:* Increased power consumption
- Increased heat output
- Instability
- Damage to the GPU
To avoid damaging the GPU, it is important to:* Start by overclocking in small increments
- Monitor the GPU’s temperature and power consumption
- Use a stable power supply
- Ensure that the GPU has adequate cooling
Memory Overclocking
Memory overclocking using XTU involves adjusting the memory’s frequency, timings, and voltage to improve performance. Higher frequencies allow for faster data transfer rates, while optimized timings reduce latency. However, overclocking requires careful consideration to ensure system stability and prevent damage.
Overclocking Settings
XTU provides several memory overclocking settings:
Frequency
Adjusts the memory’s operating frequency in MHz.
Timings
Specifies the delay between memory operations, measured in nanoseconds (ns).
Voltage
Increases the memory’s voltage to enhance stability at higher frequencies.
Overclocking Guide
To safely overclock memory:
1. Start Gradually
Increase the frequency by small increments (e.g., 100-200 MHz) and test for stability.
2. Tighten Timings
Gradually reduce timings (e.g., 1-2 ns) to minimize latency.
3. Monitor Temperature
Use XTU’s monitoring tools to ensure memory temperatures remain within safe limits.
4. Stress Test
Run memory stress tests (e.g., MemTest86) to verify stability.
Risks and Benefits
Risks:
- Overclocking can void warranties.
- Excessive voltage can damage memory modules.
- Instability can lead to system crashes or data loss.
Benefits:
- Improved memory performance and responsiveness.
- Reduced latency for faster data access.
- Potential cost savings by using lower-priced memory with overclocking headroom.
Monitoring Stability
After overclocking memory, monitor the system for stability using:
Event Viewer
Check for any errors related to memory.
XTU Monitoring Tools
Observe memory temperatures, frequency, and voltage.
Stress Tests
Regularly run memory stress tests to ensure ongoing stability.
Recommended Overclocking Settings
Optimal overclocking settings vary depending on memory type and capabilities. Consider the following recommendations:
| Memory Type | Frequency Range | Timings Range | Voltage Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDR4 | 2133-3200 MHz | 15-18-18-36 ns | 1.2-1.4 V |
| DDR5 | 4800-6400 MHz | 36-40-40-80 ns | 1.1-1.3 V |
Remember to overclock cautiously, monitor stability, and understand the risks and benefits involved.
Undervolting

Undervolting involves reducing the voltage supplied to the processor or other components below the manufacturer’s default settings. This can help reduce power consumption, temperatures, and improve system stability.
To undervolt using XTU, follow these steps:
Voltage Offset Settings
- Open XTU and navigate to the “Voltage Offset” tab.
- Locate the “Core Voltage” setting and adjust the value in millivolts (mV) to a negative value (e.g.,
0.100 mV).
- Click “Apply” to save the changes.
Stability Testing
After undervolting, it’s crucial to perform stability tests to ensure the system remains stable under load. Use stress testing software such as Prime95 or AIDA64 to run tests for several hours.
If the system becomes unstable, increase the voltage offset in small increments (e.g., +0.025 mV) until stability is restored.
Monitoring and Fine-tuning
Monitor temperatures and performance using XTU’s monitoring tools. If temperatures remain within acceptable limits and performance is satisfactory, you can gradually reduce the voltage offset further to achieve optimal undervolting settings.
Stress Testing and Stability
Stress testing is crucial after overclocking to ensure system stability. It involves running demanding workloads to identify potential errors or instability issues. Stability testing verifies that the overclocked system operates reliably under prolonged use.
XTU Stress Testing
XTU provides stress testing capabilities through its ‘Stress Test’ tab. To perform a stress test:
- Select the desired stress test type (CPU, Cache, Memory, or System).
- Adjust stress test duration and other settings as needed.
- Click ‘Start Stress Test’ and monitor system parameters during the test.
- Observe any errors or instability during the test. If errors occur, reduce overclock settings and retest until the system becomes stable.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Overclocking can sometimes lead to system instability or other issues. It is important to be aware of these potential problems and know how to troubleshoot them.Common issues that may occur during overclocking include:
- System instability
- Blue screens of death (BSODs)
- Random reboots
- Overheating
- Performance degradation
Troubleshooting Tips
If you encounter any of these issues, there are a few things you can do to troubleshoot the problem:
- Start by resetting your BIOS settings to default.This will undo any changes you have made to your overclocking settings and return your system to a stable state.
- If resetting your BIOS settings does not resolve the problem, try reducing your overclocking settings.Start by reducing the multiplier by one step and see if that resolves the issue. If it does, you can gradually increase the multiplier until you find the highest stable setting.
- If you are still having problems, try increasing the voltage to your CPU or GPU.This can help to stabilize the system and prevent crashes. However, be careful not to increase the voltage too much, as this can damage your hardware.
- If you are still unable to resolve the problem, you may need to contact Intel customer support.They can help you troubleshoot the problem and find a solution.
Troubleshooting Table
The following table lists some common overclocking issues, their causes, and potential solutions:| Issue| Cause| Solution||—|—|—|| System instability | Overclocking settings are too aggressive | Reduce overclocking settings || Blue screens of death (BSODs) | Unstable overclocking settings | Reset BIOS settings to default || Random reboots | Overheating | Increase cooling || Overheating | Inadequate cooling | Increase cooling || Performance degradation | Overclocking settings are too conservative | Increase overclocking settings |
Identifying and Resolving System Instability Caused by Overclocking
If you are experiencing system instability after overclocking, there are a few things you can do to identify and resolve the problem:
- Use a stress testing tool to test the stability of your system.This will help you to identify any unstable settings.
- If you find any unstable settings, try reducing them until the system is stable.
- If you are still having problems, try increasing the voltage to your CPU or GPU.This can help to stabilize the system and prevent crashes. However, be careful not to increase the voltage too much, as this can damage your hardware.
- If you are still unable to resolve the problem, you may need to contact Intel customer support.They can help you troubleshoot the problem and find a solution.
Warning:Overclocking can potentially damage your hardware. It is important to proceed with caution and to be aware of the risks involved. If you are not comfortable overclocking your system, it is best to leave it at its default settings.
XTU Profiles and Presets
XTU profiles and presets are powerful features that allow users to tailor their system’s performance settings to meet their specific needs. Profiles are collections of settings that can be easily applied to the system, while presets are pre-configured profiles that have been optimized for specific use cases.
Creating and Managing Profiles
Creating a custom profile is simple. Simply click on the “Profiles” tab in XTU and then click on the “New” button. You can then give the profile a name and description and start adjusting the settings. Once you have finished making changes, click on the “Save” button to save the profile.You can also manage existing profiles by clicking on the “Profiles” tab and then selecting the profile you want to manage.
You can then edit the profile’s settings, delete the profile, or share the profile with other users.
Using Preset Profiles
XTU comes with a number of preset profiles that have been optimized for different use cases. For example, there is a preset profile for gaming, a preset profile for overclocking, and a preset profile for power saving.To use a preset profile, simply click on the “Profiles” tab in XTU and then select the preset profile you want to use.
XTU will then automatically apply the settings from the preset profile to your system.
Benefits of Using Profiles and Presets
There are several benefits to using XTU profiles and presets, including:* Improved performance: Profiles and presets can help you improve the performance of your system by optimizing the settings for your specific needs.
Increased stability
Profiles and presets can help you increase the stability of your system by preventing crashes and other errors.
Easier overclocking
The Intel Extreme Tuning Utility provides comprehensive system monitoring and overclocking capabilities. To effectively utilize this utility, it is crucial to understand the various parameters and settings involved. Additionally, it is important to consider the utilities included in rent, such as electricity, water, and gas.
By understanding these utilities and their potential impact on system performance, users can optimize their Intel Extreme Tuning Utility settings to maximize performance while maintaining stability. For more information on utilities included in rent, refer to this resource.
Profiles and presets can make it easier to overclock your system by providing you with a starting point for your settings.
Sharing best practices
Profiles and presets can be shared with other users, allowing you to collaborate with others and share best practices.
“XTU profiles and presets are essential tools for optimizing system performance and stability. By leveraging these features, users can unlock the full potential of their hardware and achieve the best possible computing experience.”
John Smith, Hardware Engineer
Advanced Features
Beyond basic overclocking, XTU offers advanced features that provide even greater control over system performance. These features include curve optimization and load-line calibration, which can help users achieve higher levels of stability and performance.
However, it’s important to note that these advanced features can also increase the risk of system instability if not used properly. Therefore, it’s recommended that users only enable these features if they are familiar with the potential risks and have a good understanding of their system’s capabilities.
Curve Optimization
Curve optimization allows users to adjust the voltage-frequency curve of their CPU. This can help improve performance by allowing the CPU to operate at higher frequencies at lower voltages. However, it’s important to note that curve optimization can also increase the risk of system instability if not used properly.
To use curve optimization, users must first enable the “Advanced Tuning” option in XTU. Once enabled, users can adjust the voltage-frequency curve by clicking on the “Curve Optimizer” tab. The curve can be adjusted by dragging the points on the graph up or down.
Increasing the voltage will allow the CPU to operate at higher frequencies, while decreasing the voltage will reduce the risk of system instability.
Load-Line Calibration
Load-line calibration (LLC) is a feature that helps to reduce voltage droop under load. This can help improve performance by ensuring that the CPU receives a consistent voltage supply, even under heavy load. However, it’s important to note that LLC can also increase the risk of system instability if not used properly.
To use LLC, users must first enable the “Advanced Tuning” option in XTU. Once enabled, users can adjust the LLC setting by clicking on the “Voltage” tab. The LLC setting can be adjusted from “Auto” to “Level 8”. Higher LLC levels will reduce voltage droop under load, but they can also increase the risk of system instability.
For those interested in tweaking their system’s performance, the Intel Extreme Tuning Utility offers comprehensive controls. Whether you’re a seasoned overclocker or a novice looking to optimize your settings, this utility provides a user-friendly interface. However, it’s important to note that when renting a property, it’s crucial to clarify whether utilities such as electricity, gas, and water are included in the rent.
Are utilities included in rent ? This information can be found in the lease agreement or by consulting with the landlord. Understanding the utility arrangements will help you budget effectively and avoid unexpected expenses. Additionally, the Intel Extreme Tuning Utility allows for real-time monitoring of system parameters, enabling you to track performance metrics and fine-tune your settings accordingly.
XTU for Different Processors and Motherboards
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) is compatible with a wide range of Intel processors and motherboards, offering varying levels of functionality and support.
Processor Compatibility
XTU supports most Intel Core processors, including the latest 13th Gen Raptor Lake and previous generations such as Alder Lake, Rocket Lake, Comet Lake, and Kaby Lake. However, the specific features and overclocking capabilities available may vary depending on the processor model and its unlocked or locked multiplier status.
Motherboard Compatibility, How to use intel extreme tuning utility
XTU requires a compatible motherboard with an Intel chipset that supports overclocking. The level of support and available features may vary depending on the motherboard manufacturer and model.
For optimal compatibility and stability, it is recommended to use XTU with motherboards designed for overclocking, such as those with the Intel Z-series or X-series chipsets. These motherboards typically offer more advanced BIOS settings, voltage control options, and other features that enhance the overclocking experience.
XTU vs. Other Overclocking Software
Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) is a popular overclocking software, but it is not the only option available. Other popular overclocking software includes MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II. Each software has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it is important to compare them before choosing one.One of the most important factors to consider when choosing overclocking software is the supported hardware.
XTU only supports Intel processors, while MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II support a wider range of hardware, including AMD processors and NVIDIA graphics cards.Another important factor to consider is the overclocking options. XTU offers a wide range of overclocking options, including the ability to adjust the core voltage, core clock, and memory clock.
MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II also offer a wide range of overclocking options, but they may not be as comprehensive as XTU.The monitoring capabilities of overclocking software are also important to consider. XTU offers a wide range of monitoring options, including the ability to monitor the core temperature, core voltage, and memory clock.
MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II also offer a wide range of monitoring options, but they may not be as comprehensive as XTU.The user interface of overclocking software is also important to consider. XTU has a user-friendly interface that is easy to navigate.
MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II also have user-friendly interfaces, but they may not be as intuitive as XTU.The stability of overclocking software is also important to consider. XTU is a stable overclocking software that is unlikely to cause system crashes.
MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II are also stable overclocking software, but they may not be as stable as XTU.
Comparison Table
The following table compares the key features of XTU, MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, and ASUS GPU Tweak II:| Feature | XTU | MSI Afterburner | EVGA Precision X1 | ASUS GPU Tweak II ||—|—|—|—|—|| Supported hardware | Intel processors | AMD processors and NVIDIA graphics cards | AMD processors and NVIDIA graphics cards | AMD processors and NVIDIA graphics cards || Overclocking options | Wide range of overclocking options, including the ability to adjust the core voltage, core clock, and memory clock | Wide range of overclocking options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU | Wide range of overclocking options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU | Wide range of overclocking options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU || Monitoring capabilities | Wide range of monitoring options, including the ability to monitor the core temperature, core voltage, and memory clock | Wide range of monitoring options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU | Wide range of monitoring options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU | Wide range of monitoring options, but may not be as comprehensive as XTU || User interface | User-friendly interface that is easy to navigate | User-friendly interface, but may not be as intuitive as XTU | User-friendly interface, but may not be as intuitive as XTU | User-friendly interface, but may not be as intuitive as XTU || Stability | Stable overclocking software that is unlikely to cause system crashes | Stable overclocking software, but may not be as stable as XTU | Stable overclocking software, but may not be as stable as XTU | Stable overclocking software, but may not be as stable as XTU |
Conclusion
XTU is a powerful and stable overclocking software that is ideal for beginners and experienced overclockers alike. However, it is important to note that XTU only supports Intel processors. If you are using an AMD processor or an NVIDIA graphics card, you will need to use a different overclocking software, such as MSI Afterburner, EVGA Precision X1, or ASUS GPU Tweak II.
Top FAQs
What is the primary function of Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU)?
XTU is a software tool designed to monitor, adjust, and optimize system parameters, including overclocking settings, for enhanced performance and stability.
Can XTU be used to overclock both CPUs and GPUs?
Yes, XTU provides comprehensive overclocking capabilities for both CPUs and GPUs, allowing users to fine-tune their systems for specific workloads and applications.
What are the potential risks associated with overclocking?
Overclocking can potentially lead to system instability, reduced component lifespan, and even hardware damage if not performed correctly. It is crucial to proceed with caution and follow recommended guidelines.
How can I ensure system stability after overclocking with XTU?
XTU offers stress testing and stability testing features to help users verify system stability after overclocking. It is recommended to run these tests thoroughly to identify any potential issues.
What are the benefits of using XTU profiles and presets?
XTU profiles and presets allow users to save and share customized overclocking settings, simplifying the process and enabling quick and easy optimization for different scenarios.


