What does it mean to collate when printing – Collating in printing, an essential process often overlooked, plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and organization of printed materials. This guide delves into the intricacies of collation, exploring its methods, equipment, and significance in the printing industry.
From understanding the concept of gathering and assembling printed sheets to selecting the appropriate collation method for specific print jobs, this comprehensive guide provides valuable insights and practical advice for printers and professionals alike.
Definition of Collating in Printing: What Does It Mean To Collate When Printing
Collating in printing refers to the process of gathering and arranging printed sheets in the correct order to form a complete document or publication. This involves ensuring that the pages are assembled in the proper sequence, with any additional components, such as covers, inserts, or other materials, included in their designated places.
Collated printed materials can include books, magazines, brochures, catalogs, and other types of publications. The process of collating can be done manually or with the use of automated machines, depending on the volume and complexity of the job.
Importance of Collating
Collating is an important step in the printing process as it ensures that the final product is complete and accurate. Proper collation helps to prevent errors such as missing pages, out-of-order pages, or incorrect assembly. It also ensures that the publication is visually appealing and easy to navigate for readers.
Collation Methods
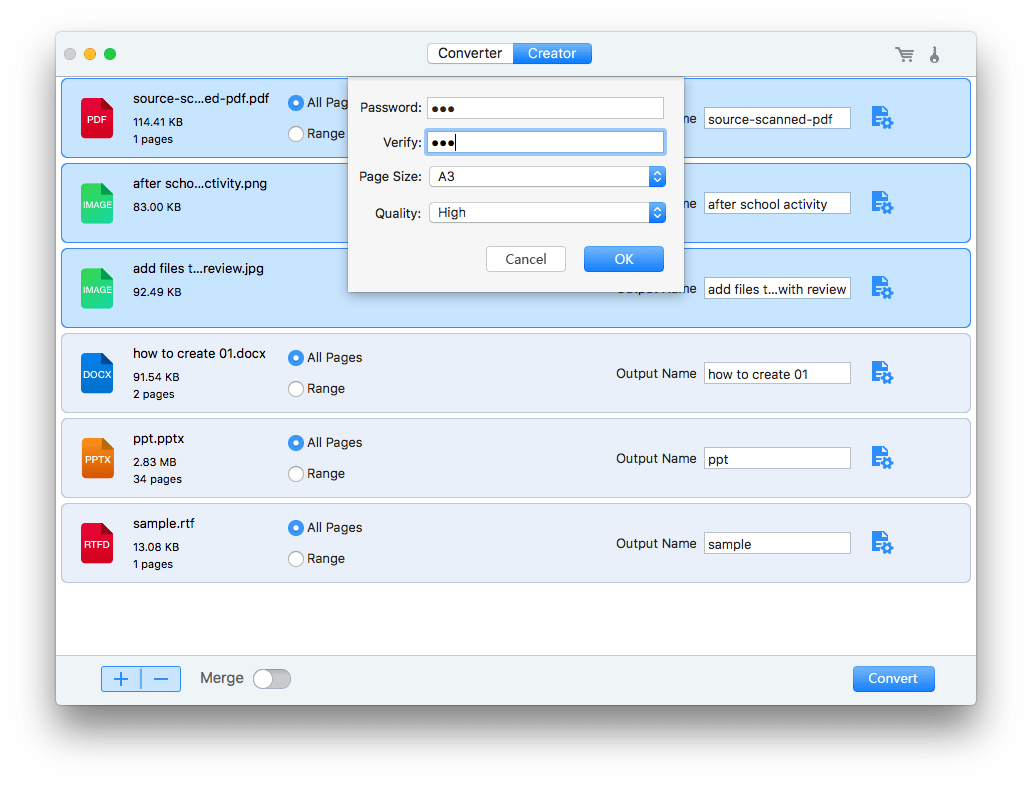
Collation is the process of assembling printed sheets in the correct order to form a complete document. There are various methods used for collating printed sheets, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
Manual Collation
Manual collation is the most basic and labor-intensive method of collating. It involves manually gathering and assembling the printed sheets in the correct order, one sheet at a time. This method is suitable for small print runs or when accuracy is critical, but it can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Semi-Automatic Collation
Semi-automatic collation involves using a machine to assist in the collation process. The machine aligns and feeds the printed sheets into a stack, and the operator manually gathers and assembles the sheets in the correct order. This method is faster than manual collation but still requires some manual labor.
Automatic Collation
Automatic collation is the most efficient and automated method of collating. The machine automatically aligns, feeds, and assembles the printed sheets in the correct order, without any manual intervention. This method is suitable for large print runs and provides the highest level of accuracy and productivity.
Collation Equipment
Collation equipment plays a crucial role in the printing industry, enabling the efficient assembly and organization of printed sheets into complete sets.
There are various types of collation equipment, each designed for specific applications and production volumes. These include gathering machines, stitchers, and perfect binders.
Gathering Machines
Gathering machines are used to gather individual printed sheets in the correct sequence and order. They typically consist of multiple stations, each holding a stack of sheets. As the sheets are fed into the machine, they are collated and stacked together.
Gathering machines offer high speed and accuracy, making them suitable for large-volume production runs. They can handle a wide range of paper sizes and weights, and some models can also insert pre-printed covers or inserts.
Stitchers
Stitchers are used to bind collated sheets together using staples. They are available in various sizes and capacities, from small desktop models to high-volume industrial machines.
Stitchers offer a cost-effective and efficient way to bind documents. They are commonly used for booklets, brochures, and other types of publications.
Perfect Binders
Perfect binders are used to create a professional-looking, bound document with a glued spine. They are typically used for books, magazines, and other high-quality publications.
Perfect binders offer a durable and attractive binding solution. They can handle a wide range of paper sizes and weights, and some models can also add covers and other finishing touches.
Selection of Collation Equipment
The choice of collation equipment depends on several factors, including the volume of production, the type of document being produced, and the desired level of automation.
For small-volume production runs, a simple gathering machine or stitcher may be sufficient. For larger production runs, a perfect binder may be a better choice.
Collating when printing refers to the process of arranging printed pages in a specific order, ensuring that each set of pages is complete and in the correct sequence. This process is commonly used in printing multiple copies of a document, such as a book or a magazine, where it is essential to maintain the order of the pages for easy reading and comprehension.
To understand the concept of collating when printing, it is helpful to refer to resources like what does collate mean printing , which provide detailed explanations and examples of the collating process in different printing scenarios.
Real-World Applications
Collation equipment is used in a wide range of industries, including:
- Printing and publishing
- Office administration
- Education
- Manufacturing
Collation Standards
Collation standards in printing are crucial for ensuring the correct assembly and organization of printed materials. They establish industry-accepted guidelines and quality control measures to maintain consistency, accuracy, and efficiency throughout the collation process.Adhering to collation standards helps prevent errors, such as missing or misordered pages, which can lead to costly reprints and customer dissatisfaction.
Standardized procedures and equipment ensure that printed materials are assembled in the intended sequence, ensuring their usability and readability.
Industry-Accepted Guidelines
Various industry organizations, such as the Printing Industries of America (PIA) and the International Standards Organization (ISO), have established guidelines for collation. These guidelines cover aspects such as:
- Page sequence and orientation
- Use of collating marks or symbols
- Quality control procedures
By following these guidelines, printing companies can ensure their collation practices meet industry best practices.
Quality Control Measures
Effective quality control measures are essential for maintaining collation standards. These measures include:
- Visual inspection of printed materials
- Automated collation equipment with error detection capabilities
- Regular calibration and maintenance of collation equipment
Implementing these quality control measures helps minimize the risk of errors and ensures the delivery of high-quality, properly collated printed materials.
Benefits of Collation
/shutterstock_576831907Converted-5a42bd19494ec900366a90fb.png)
Collation, the process of assembling printed materials in a specific order, offers numerous advantages in various industries. By organizing printed documents, collation improves efficiency, reduces errors, enhances quality, and streamlines processes.
One significant benefit of collation is increased efficiency. It allows for the quick and accurate assembly of large volumes of printed materials, saving time and labor costs. Collation eliminates the need for manual sorting and reduces the risk of misplacing or losing documents.
Error Reduction
Collation plays a crucial role in error reduction. By ensuring that printed materials are assembled in the correct order, collation minimizes the chances of errors and inconsistencies. This is particularly important for sensitive documents, such as legal contracts or financial statements, where accuracy is paramount.
Enhanced Quality
Collation contributes to the overall quality of printed materials. Well-collated documents appear professional and organized, making a positive impression on recipients. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses that want to project a polished and efficient image.
Successful Implementations
Collation has been successfully implemented in various industries, including publishing, education, and healthcare. In publishing, collation ensures that books, magazines, and other printed materials are assembled in the correct order before binding. In education, collation is used to organize student handouts, tests, and other learning materials.
In healthcare, collation helps organize patient records, medical reports, and other sensitive documents.
Challenges in Collation

Collation processes can encounter various challenges that hinder the efficient and accurate assembly of printed materials. These challenges can arise from data-related issues or limitations in the collation equipment or processes.
Data Inconsistencies
Data inconsistencies occur when there are discrepancies or mismatches in the data used for collation. These inconsistencies can manifest as errors in data entry, formatting, or data types, leading to difficulties in matching and assembling the correct components.
- Solutions:Implementing data validation and cleaning processes to identify and correct errors, ensuring data integrity and consistency.
- Best Practices:Establishing clear data standards and guidelines to minimize the occurrence of inconsistencies, ensuring data accuracy and compatibility.
Missing or Incomplete Data
Missing or incomplete data refers to the absence of certain data elements or fields required for collation. This can occur due to data entry errors, data loss during transmission, or incomplete data sources.
Collating when printing refers to the process of gathering and arranging printed pages in the correct order. This process is crucial to ensure that the printed document is coherent and easy to read. If you encounter ink stains on your clothes during the printing process, you can find helpful tips on removing them at how can you get ink stains out of clothes.
Once the stains are removed, you can continue collating the printed pages to complete the document.
- Solutions:Employing data imputation techniques to estimate or fill in missing data, preserving the integrity of the collation process.
- Best Practices:Implementing data quality checks to identify and address missing or incomplete data before collation, ensuring a complete and accurate dataset.
Data Duplication
Data duplication occurs when multiple instances of the same data element or record exist within the collation dataset. This can lead to errors in assembly and incorrect printed materials.
- Solutions:Utilizing data deduplication techniques to identify and remove duplicate data, ensuring the uniqueness and accuracy of the collation dataset.
- Best Practices:Implementing data integrity constraints and unique identifiers to prevent data duplication during data entry and processing.
Data Format Incompatibilities
Data format incompatibilities arise when data from different sources or systems uses different formats or structures. This can hinder the collation process, as the data cannot be easily matched or merged.
- Solutions:Implementing data standardization processes to convert data into a common format, ensuring compatibility and seamless collation.
- Best Practices:Establishing data exchange standards and guidelines to facilitate the interoperability of data from various sources.
– Explain how collation requirements vary based on print job specifications, including
Collation requirements can vary significantly based on the specifications of a print job. Some of the key factors that influence collation requirements include:
Number of copies:The number of copies required for a print job will determine the number of sets that need to be collated. For example, a print job that requires 100 copies will need to be collated into 100 sets.
Page order:The order of the pages in a print job is also important for collation. The pages need to be collated in the correct order so that the document is easy to read and understand. For example, a business proposal may need to be collated in the following order: cover page, executive summary, table of contents, introduction, body, conclusion, and appendix.
Duplex printing:Duplex printing is a printing method that prints on both sides of a sheet of paper. If a print job is being printed duplex, the pages need to be collated in a specific order so that the pages are printed on the correct sides of the paper.
For example, a brochure may need to be collated in the following order: front cover, inside front cover, page 1, page 2, page 3, page 4, inside back cover, back cover.
Stapling:Stapling is a common way to bind collated pages together. The type of stapling that is used will depend on the thickness of the document and the desired finished look. For example, a business proposal may be stapled in the top left corner, while a catalog may be stapled in the spine.
Collation and Binding
Collation and binding are two closely related processes in printing. Collation refers to the process of gathering and assembling printed sheets in the correct order, while binding refers to the process of securing the sheets together to form a book or booklet.
Collation is an important step in the printing process because it ensures that the finished product is complete and accurate. If the sheets are not collated correctly, the book or booklet may be difficult to read or even impossible to use.
Binding Methods
The type of binding used will depend on the size, shape, and purpose of the book or booklet. Some common binding methods include:
- Perfect binding: This is the most common type of binding used for books and booklets. The sheets are glued together at the spine, and a cover is then added.
- Saddle stitching: This type of binding is used for booklets and pamphlets. The sheets are stapled together at the spine.
- Spiral binding: This type of binding is used for books and booklets that need to be able to lay flat. The sheets are bound together with a spiral wire.
- Hard cover binding: This type of binding is used for books that are meant to be durable. The sheets are bound together with a hard cover.
The choice of binding method will also affect the collation process. For example, perfect binding requires the sheets to be collated in a specific order, while saddle stitching does not.
Digital Collation
The advent of digital printing has revolutionized the collation process. Digital printing allows for the printing of documents directly from a computer file, eliminating the need for physical printing plates. This has led to a number of changes in the way that collation is performed.
One of the main advantages of digital collation is that it is much more flexible than traditional collation methods. With digital collation, it is possible to create custom collation sequences that are tailored to the specific needs of the print job.
This is particularly useful for complex print jobs that require multiple different collation sequences.
Advantages of Digital Collation
- Flexibility: Digital collation allows for the creation of custom collation sequences that are tailored to the specific needs of the print job.
- Speed: Digital collation is much faster than traditional collation methods, as it does not require the manual sorting and assembly of printed sheets.
- Accuracy: Digital collation is more accurate than traditional collation methods, as it is less prone to human error.
- Cost-effectiveness: Digital collation can be more cost-effective than traditional collation methods, especially for large print jobs.
Limitations of Digital Collation
- Equipment costs: Digital collation equipment can be expensive, which can make it a less viable option for small print shops.
- File size: Digital collation requires the use of large digital files, which can be difficult to manage and store.
- Compatibility: Digital collation equipment may not be compatible with all types of printers and paper stocks.
Collation in Offset Printing
Offset printing collation involves gathering and assembling printed sheets in the correct order to create complete sets of printed materials. It is a crucial step in the printing process, ensuring that the final product is accurate and ready for binding or distribution.In offset printing, collation is typically performed manually or using automated equipment.
Manual collation requires careful attention to detail and can be time-consuming for large print runs. Automated collation machines can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy, especially for complex projects with multiple pages or sections.
Challenges in Offset Printing Collation
Offset printing collation can present several challenges, including:
Paper Misalignment
Ensuring that the sheets are aligned precisely is essential to prevent errors and maintain the quality of the final product.
Sheet Damage
Collation processes can sometimes damage the printed sheets, especially if they are handled roughly or not properly aligned.
Time Constraints
Collation can be a time-consuming process, especially for large print runs or complex projects.
Best Practices for Offset Printing Collation
To overcome these challenges and ensure successful collation in offset printing, several best practices should be followed:
Proper Planning
Careful planning and preparation are crucial for efficient collation. The collation sequence should be determined in advance, and the necessary equipment and resources should be available.
Accurate Printing
Ensuring that the printed sheets are accurate and free of errors is essential to avoid costly reprints or delays.
Proper Equipment
Using the right collation equipment for the specific job is important. Automated collation machines can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy, especially for large print runs.
Careful Handling
Printed sheets should be handled carefully throughout the collation process to prevent damage or misalignment.
Quality Control
Implementing a quality control process to inspect the collated sets for accuracy and completeness is crucial to ensure the final product meets the desired standards.
Collation in Web Printing
Collation in web printing poses unique challenges due to the continuous nature of the printing process and the high speeds involved. Unlike sheet-fed printing, where each sheet is printed and collated separately, web printing involves printing on a continuous roll of paper, which is then cut and collated into individual sets.
Methods and Equipment for Web Printing Collation
Web printing collation methods include:
- Inline Collation:This method uses a collating unit integrated into the printing press. As the printed web passes through the press, it is cut and collated into sets, which are then stacked or bundled.
- Offline Collation:This method involves cutting the printed web into individual sheets and then collating them using a separate collating machine. Offline collation allows for greater flexibility and control over the collation process but is less efficient than inline collation.
Impact of Paper Quality and Thickness on Collation
The quality and thickness of the paper used in web printing can impact the collation process. Thicker paper may be more difficult to collate accurately, especially at high speeds. High-quality paper with consistent dimensions ensures smoother and more accurate collation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Collation Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages ||—|—|—|| Inline Collation | High efficiency, reduced labor costs | Limited flexibility, potential for errors at high speeds || Offline Collation | Greater flexibility, better control over accuracy | Lower efficiency, higher labor costs |
Troubleshooting Common Collation Issues in Web Printing
Common collation issues in web printing include:
- Misfeeds:Paper jams or misalignments during the collation process.
- Missing or Duplicated Pages:Incorrect collation sequence or skipped pages.
- Incorrect Page Order:Pages out of order within the collated sets.
Troubleshooting these issues involves checking for paper quality, proper equipment setup, and accurate cutting and collating settings.
Best Practices for Accurate and Efficient Collation in Web Printing
Best practices for accurate and efficient collation in web printing include:
- Use high-quality paper with consistent dimensions.
- Calibrate and maintain the printing press and collating equipment regularly.
- Monitor the collation process closely and make adjustments as needed.
- Implement quality control measures to ensure accuracy.
Flowchart of Web Printing Collation
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in web printing collation:
- Print the web on a printing press.
- Cut the web into individual sheets.
- Collate the sheets into sets using an inline or offline collator.
- Stack or bundle the collated sets.
Collation in Specialty Printing
Collation in specialty printing involves gathering, stitching, trimming, and folding printed sheets to create finished products like brochures, booklets, catalogs, and direct mail pieces.
Gathering
Gathering is the process of assembling printed sheets in the correct order, ensuring that all pages are present and accounted for.
Stitching
Stitching involves binding the gathered sheets together using staples, thread, or other binding methods to create a secure and durable product.
Trimming
Trimming involves cutting the edges of the printed sheets to create a clean and finished appearance, removing any excess paper or ragged edges.
Folding
Folding involves creating creases in the printed sheets to create brochures, booklets, or other folded products. Folding can be done manually or using specialized folding machines.
Examples of Specialty Printing Applications that Require Collation
- Brochures: Collation is essential for assembling the multiple pages of a brochure in the correct order and binding them together.
- Booklets: Collation ensures that the pages of a booklet are gathered in the correct sequence and stitched or bound together.
- Catalogs: Collation is crucial for organizing the numerous pages of a catalog in the proper order and binding them securely.
- Direct mail pieces: Collation is necessary for assembling direct mail pieces, such as postcards or flyers, and ensuring that they are ready for mailing.
Future Trends in Collation
The future of collation is being shaped by emerging technologies and trends such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), robotic process automation (RPA), and blockchain. These technologies have the potential to revolutionize collation processes, making them more efficient, cost-effective, and accurate.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.Cloud computing can be used to host collation software and data, making it accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
This can improve collaboration between team members and reduce the need for physical storage space.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are technologies that allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time. These technologies can be used to automate collation tasks, such as sorting and matching documents. This can free up human workers to focus on more complex tasks.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is a technology that uses software robots to automate repetitive tasks. These robots can be used to perform collation tasks, such as extracting data from documents and entering it into a database. This can improve accuracy and consistency and reduce the risk of errors.
Blockchain
Blockchain is a distributed database that is used to maintain a continuously growing list of records, called blocks. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks, which requires collusion of the network majority.Blockchain can be used to create a secure and transparent record of collation transactions.
This can help to improve trust and accountability in the collation process.
Challenges and Opportunities, What does it mean to collate when printing
The adoption of new technologies in collation also presents some challenges. One challenge is the need to invest in new equipment and software. Another challenge is the need to train staff on how to use these new technologies.Despite these challenges, the benefits of adopting new technologies in collation are significant.
These technologies can help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve accuracy and consistency.
Predictions
The future of collation is bright. Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize the way that collation is done. These technologies will make collation more efficient, cost-effective, and accurate. As a result, collation will become an increasingly important part of the printing process.
Key Trends and Predictions
- The use of cloud computing, AI, ML, RPA, and blockchain will become more widespread in the collation industry.
- These technologies will help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve accuracy and consistency.
- Collation will become an increasingly important part of the printing process.
Case Studies and Examples
Collation plays a crucial role in ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of printing processes. Several case studies and examples highlight the importance and impact of collation in printing:
Innovative Collation Solutions
* Automated Collation Systems:In a high-volume printing environment, automated collation systems streamline the process by using robotic arms or conveyor belts to assemble printed materials accurately and efficiently. This reduces labor costs, minimizes errors, and increases productivity.* Cloud-Based Collation Management:Cloud-based platforms enable remote management and tracking of collation processes.
Printers can monitor the status of collation jobs, access real-time data, and make adjustments as needed, improving collaboration and reducing downtime.
Efficient Collation Practices
* Digital Collation:Digital printing allows for on-demand collation, eliminating the need for large print runs and reducing waste. Digital presses can produce collated sets in small quantities, reducing inventory costs and providing greater flexibility.* Optimized Collation Sequencing:By optimizing the sequence of collation, printers can minimize the number of passes required and reduce the risk of errors.
This involves grouping similar documents or pages together and using efficient sorting algorithms.* Barcode Tracking:Barcodes can be printed on each printed piece, enabling automated tracking and verification during the collation process. This ensures accuracy and reduces the risk of missing or misplaced documents.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of collation in printing?
Collation ensures that printed sheets are assembled in the correct order, ensuring the accuracy and organization of printed materials.
What are the different methods of collation?
Collation methods include manual, semi-automatic, and automatic, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
What equipment is used for collation?
Collation equipment includes gathering machines, stitchers, and perfect binders, which vary in speed, capacity, and automation capabilities.
How do I choose the right collation method for my print job?
Factors to consider when choosing a collation method include the number of copies, page order, duplex printing, and stapling requirements.
What are some tips for effective collation?
Tips for effective collation include ensuring accuracy, handling and storing collated materials properly, and troubleshooting common collation problems.


