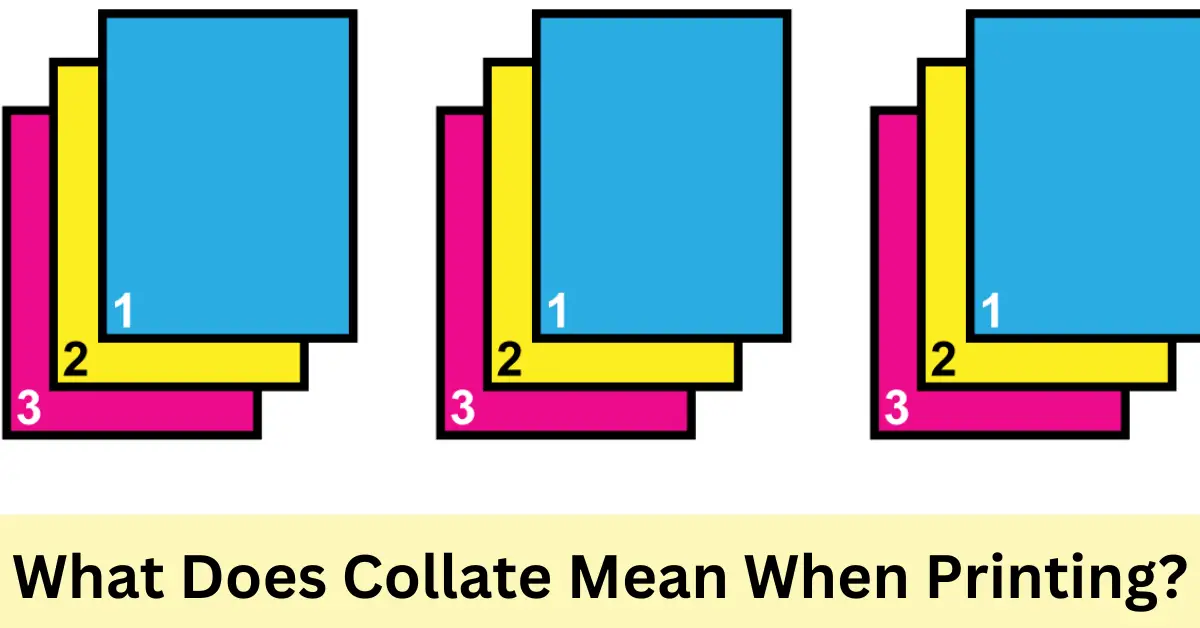
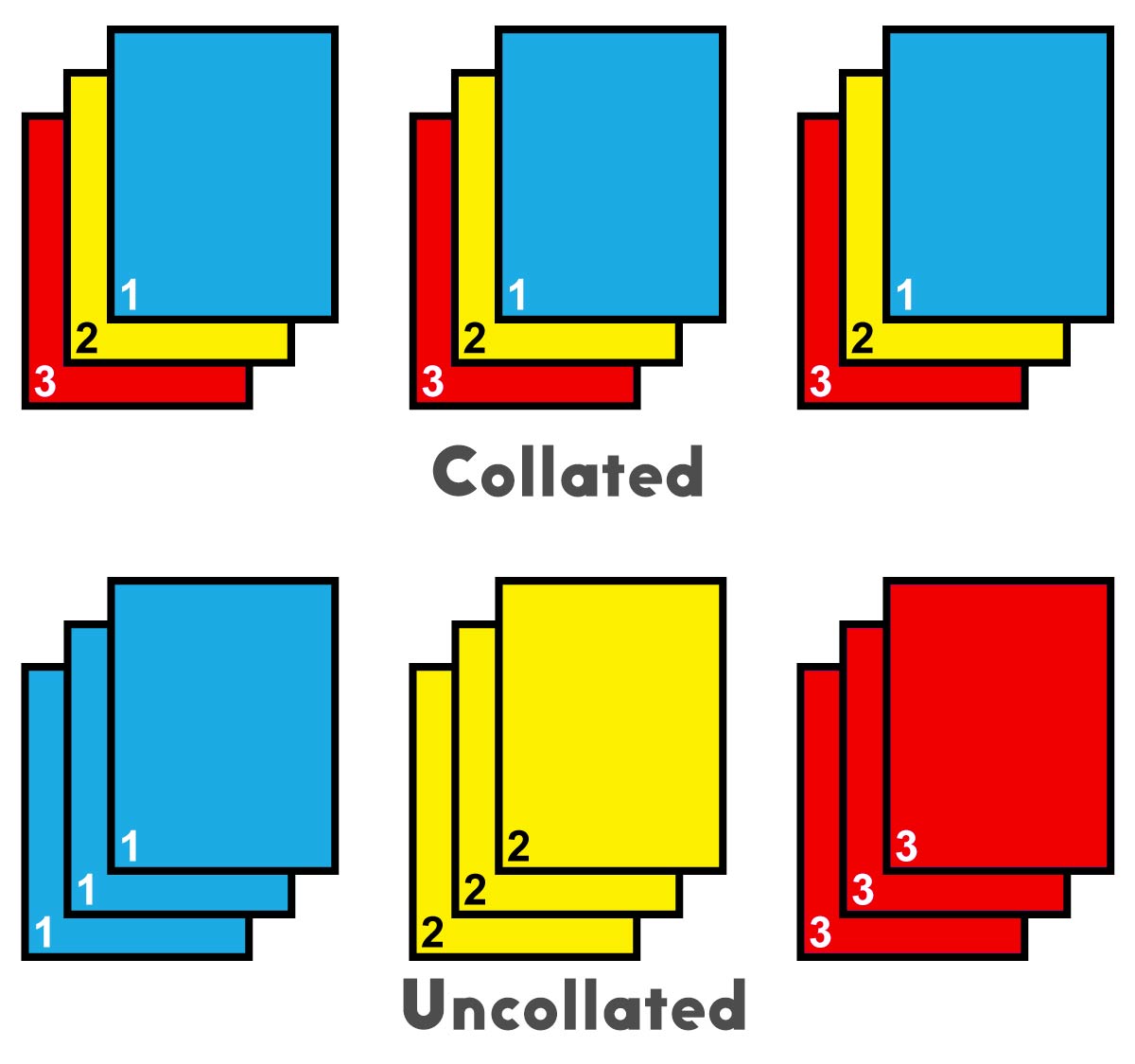
What does printing collate mean? Collating is a crucial post-press process in printing that involves gathering and arranging printed sheets in a specific order to create a complete document. It plays a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and organization of printed materials, from simple documents to complex publications.
This guide delves into the intricacies of printing collation, exploring its definition, purpose, advantages, and disadvantages. We’ll also discuss various collating techniques, equipment, and industry standards, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential printing process.
Definition of Collating
Collating in printing refers to the process of arranging and assembling printed sheets in the correct order and sequence to create a complete document. It involves gathering the individual pages or sections of a printed document and arranging them in the proper order, ensuring that all pages are present and accounted for.
Purpose of Collating
The primary purpose of collating is to organize and prepare printed materials for binding or further processing. Collating ensures that all pages are in the correct order, making it easier to assemble and navigate the final document. It helps prevent errors and ensures that the finished product is complete and ready for use.
Examples of Collated Printed Materials
Examples of collated printed materials include:
- Books and magazines
- Brochures and pamphlets
- Reports and proposals
- Legal documents
- Marketing materials
Difference between Collating and Binding
Collating is distinct from binding, which involves attaching the collated pages together to create a finished document. Collating focuses on arranging the pages in the correct order, while binding secures them together to form a cohesive unit.
Advantages of Collating
- Ensures correct page order
- Facilitates binding and assembly
- Prevents errors and omissions
- Improves document organization
Disadvantages of Collating
- Can be time-consuming for large documents
- Requires careful attention to detail
- May require specialized equipment
Step-by-Step Guide to Collating Printed Materials
- Gather all printed pages
- Sort the pages into numerical order
- Align the pages at the top or side
- Check for missing or duplicate pages
- Assemble the pages in the correct sequence
Methods of Collation

Collation is the process of gathering and arranging printed sheets in the correct order for binding. There are three main methods of collation: manual, semi-automatic, and automatic.
Manual collationis the most labor-intensive method, but it is also the most accurate. In manual collation, each sheet is collated by hand, one at a time. This method is typically used for small print runs or for jobs that require special handling.
Semi-automatic collationis a more efficient method than manual collation, but it is not as accurate. In semi-automatic collation, a machine gathers the sheets and collates them into sets. The operator then checks the sets for accuracy and makes any necessary corrections.
Automatic collationis the most efficient method of collation, but it is also the most expensive. In automatic collation, a machine gathers, collates, and stacks the sheets into sets. The operator only needs to load the sheets into the machine and remove the finished sets.
The following table compares the advantages and disadvantages of each collation method:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Manual | Accurate, allows for special handling | Labor-intensive, slow |
| Semi-automatic | More efficient than manual, still allows for some accuracy | Not as accurate as manual, requires operator checking |
| Automatic | Most efficient, hands-off | Most expensive, not as accurate as manual or semi-automatic |
Collating Equipment

Collating equipment refers to the various types of machines and devices used to gather, assemble, and arrange printed materials in the correct order and sequence.
These machines play a crucial role in the post-printing process, ensuring that printed documents, brochures, booklets, and other materials are ready for distribution and use.
Types of Collating Equipment
- Manual Collators:As the name suggests, these are hand-operated machines that require manual intervention to gather and assemble printed sheets.
- Semi-Automatic Collators:These machines combine manual and automated processes. They use a combination of operator input and automated functions to gather and assemble printed sheets.
- Fully Automatic Collators:These machines are designed to automate the entire collating process. They use advanced technology, such as optical sensors and robotic arms, to gather and assemble printed sheets with minimal human intervention.
Functions of Collating Equipment
- Gathering:Collating equipment gathers printed sheets from multiple sources and assembles them in the correct order.
- Jogging:The collating process involves aligning and straightening the printed sheets before assembling them.
- Stitching or Stapling:Some collating machines can also perform stitching or stapling operations to bind the assembled sheets together.
- Counting:Collating equipment often includes counting mechanisms to ensure that the correct number of sheets are gathered and assembled.
Images or Diagrams of Collating Equipment
[Provide images or diagrams of different types of collating equipment, including manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic models.]
Collation Order

Collation order refers to the specific sequence in which printed materials are arranged and assembled. Several factors influence the collation order, including the document’s structure, content, and intended purpose.
Maintaining proper collation order is crucial to ensure that the printed materials are organized logically and easy to navigate. It helps readers find the information they need quickly and efficiently.
s
- Factors Determining Collation Order
- Importance of Maintaining Proper Collation Order
- Examples of Different Collation Orders
- Steps Involved in Collating Printed Materials
- Troubleshooting Common Collation Errors
- Table Summarizing Different Collation Methods
- Flowchart Illustrating the Collation Process
- Glossary of Terms Related to Collation
Collation Standards
The printing industry has established standards to ensure that printed materials are collated in a consistent and accurate manner. These standards specify the order in which pages should be arranged, the orientation of the pages, and the method of binding.
Adhering to these standards is essential for ensuring that printed materials are easy to read, assemble, and use.
Benefits of Adhering to Collation Standards
- Ensures consistency and accuracy in the collation process
- Makes it easier to assemble and use printed materials
- Reduces the risk of errors and omissions
- Improves the overall quality of printed materials
Consequences of Not Meeting Collation Standards
- Can lead to confusion and frustration for users
- Can make it difficult to assemble and use printed materials
- Can increase the risk of errors and omissions
- Can damage the reputation of the printer
Troubleshooting Collation Problems
Collation problems can arise due to various factors, such as incorrect settings, hardware issues, or software glitches. Identifying and resolving these issues promptly is crucial to ensure efficient printing operations.
Common collation problems include misaligned pages, incomplete sets, and incorrect page order. These issues can be caused by factors such as incorrect paper orientation, faulty collators, or software configuration errors.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Verify paper orientation and ensure it aligns with the printer’s settings.
- Inspect the collator for any physical damage or misalignment.
- Check software settings for collation options and ensure they correspond with the desired output.
- Restart the printer and software to clear any temporary glitches.
- Contact technical support for assistance if the issue persists.
Best Practices for Preventing Collation Errors
- Regularly calibrate the printer and collator to maintain accuracy.
- Use high-quality paper that is compatible with the printer.
- Avoid overloading the printer or collator with excessive paper.
- Train operators on proper paper handling and collation techniques.
- Implement a regular maintenance schedule to prevent equipment malfunctions.
Table: Common Collation Problems, Causes, and Solutions
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Misaligned pages | Incorrect paper orientation or faulty collator | Adjust paper orientation or inspect the collator for damage |
| Incomplete sets | Printer or collator malfunction | Restart the printer and collator or contact technical support |
| Incorrect page order | Software configuration error or collator misalignment | Check software settings and inspect the collator for proper alignment |
Code Example
// Code to resolve a collation issue caused by incorrect software settings // Get the current collation settings var settings = printer.getCollationSettings(); // Modify the collation settings as needed settings.setCollationType(CollationType.SEQUENCE); // Apply the new settings to the printer printer.setCollationSettings(settings);
Resources for Further Learning
- Adobe Acrobat Print Troubleshooting Guide
- HP Printer Collation Troubleshooting
- Lexmark Collation Troubleshooting
Automation in Collation
Automation plays a pivotal role in streamlining the collation process, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy.
The benefits of automating collation include:
- Reduced labor costs
- Increased speed and efficiency
- Improved accuracy and reduced errors
- Enhanced productivity
However, there are also challenges associated with automating collation, such as:
- High initial investment costs
- Complexity of implementation and maintenance
- Potential for errors if the system is not properly configured
Automated collation systems come in various types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Inline collation systemsare integrated into the printing press and perform collation as part of the printing process.
- Offline collation systemsare separate machines that perform collation after the printing process is complete.
- Robotic collation systemsuse robots to perform the collation process.
Automation can be used to ensure the accuracy of collation by using sensors and other technologies to verify that the correct sheets are being collated.
Automation can also be used to reduce the cost of collation by reducing the amount of labor required and by increasing the efficiency of the process.
The future trends in automation in collation include the development of more sophisticated systems that can handle a wider range of collation tasks and the integration of automation with other printing and finishing processes.
Collation for Special Projects: What Does Printing Collate Mean

Collation for special projects requires careful planning and attention to detail to ensure the final product meets the unique requirements of the project. These projects often involve non-standard materials, complex collation sequences, or specialized finishing techniques.
Handling Non-Standard Materials
Non-standard materials, such as thick cardstock, textured papers, or plastic sheets, require special handling during collation to avoid damage or misalignment. Specialized equipment, such as friction feeders or ultrasonic welders, may be necessary to handle these materials effectively.
Printing collate refers to the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order. Collation is an essential step in printing, as it ensures that the final product is organized and easy to read. Collate is a crucial step in the printing process, as it helps to ensure that the final product is organized and easy to read.
Collating printed pages involves gathering the pages in the correct order and then stapling or binding them together.
Complex Collation Requirements
Complex collation requirements, such as nested sets, variable page counts, or multiple inserts, require careful planning and execution. Manual collation may be impractical for these projects, and automated collation systems or specialized equipment may be necessary to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
Case Studies
* Custom Photo Album:A photo album with varying page counts and custom inserts required precise collation to ensure the correct photos and pages were assembled in the correct order. An automated collation system with optical character recognition (OCR) was used to identify and sort the pages and inserts, resulting in a high-quality finished product.* Limited Edition Art Book:A limited-edition art book with unique cover materials and intricate collation required specialized handling and finishing techniques.
A combination of manual and automated collation was used, along with specialized equipment for handling the delicate cover materials. The final product met the high standards of the publisher and collectors.
Collation in Different Industries
Collation finds extensive applications across various industries, each with specific requirements and challenges. Understanding these industry-specific needs is crucial for effective collation practices.
Industries that heavily rely on collation include:
- Printing and Publishing:Collation is a vital step in the production of books, magazines, brochures, and other printed materials. It ensures the correct order and sequence of pages within each document.
- Manufacturing:In manufacturing, collation is used to assemble components into finished products. For example, in the automotive industry, parts like screws, bolts, and gaskets are collated into kits for efficient assembly.
- Healthcare:Collation plays a critical role in the healthcare industry, where accurate and timely delivery of medical records, prescriptions, and test results is essential. Collation systems ensure that patient information is organized and easily accessible.
- Logistics and Shipping:Collation is crucial in the logistics industry for assembling and tracking shipments. It helps ensure that the correct items are packed together and delivered to the intended recipients.
- Retail:In the retail industry, collation is used to create product displays, assemble promotional materials, and prepare customer orders. Efficient collation practices help enhance customer satisfaction and reduce errors.
Industry-Specific Collation Challenges
Each industry faces unique challenges in collation. For instance, in the printing industry, maintaining precise page order and ensuring proper alignment are critical. In manufacturing, the durability and accuracy of collated components are paramount. In healthcare, data privacy and security are of utmost importance.
Understanding these industry-specific challenges is essential for developing tailored collation solutions.
Examples of Collated Printed Materials
- Books:Collation ensures the correct sequence of chapters, pages, and sections within a book.
- Magazines:Collation assembles articles, advertisements, and other content in the intended order.
- Brochures:Collation combines multiple printed sheets into a single, folded document.
- Catalogs:Collation organizes product information and images in a logical sequence.
- Flyers:Collation assembles multiple flyers into a single stack or booklet.
Future Trends in Collation

The future of collation is expected to witness significant advancements driven by technological innovations. Automated collation systems, inline collation, and digital collation solutions are gaining traction, offering increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved accuracy.
Automated Collation Systems
Automated collation systems utilize advanced robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate the collation process. These systems can handle large volumes of documents, sort them accurately, and assemble them in the desired order. They offer benefits such as reduced human error, increased productivity, and improved consistency.
Inline Collation
Inline collation integrates the collation process into the printing workflow. This eliminates the need for separate collation equipment and reduces handling time. Inline collation systems can be customized to meet specific requirements, such as collating documents based on variable data or inserting pre-printed materials.
Digital Collation Solutions
Digital collation solutions leverage software and digital technologies to streamline the collation process. These solutions allow users to create digital collations, which can be easily modified and shared. They also provide real-time visibility into the collation status, enabling better control and tracking.
Impact on the Printing Industry
The future of collation is closely tied to the advancements in the printing industry. Increased automation, personalized printing, and on-demand production are driving the demand for innovative collation solutions. Automated collation systems can handle the growing volume of personalized print jobs, while digital collation solutions facilitate on-demand printing and distribution.
Innovative Collation Solutions
AI-powered collation, robotic collation, and sustainable collation methods are among the emerging innovative collation solutions. AI-powered collation systems use machine learning algorithms to optimize the collation process, reducing errors and improving efficiency. Robotic collation utilizes robots to automate the physical collation tasks, increasing speed and accuracy.
Sustainable collation methods focus on reducing waste and environmental impact by using eco-friendly materials and optimizing the collation process.
Printing collate is the process of arranging printed pages in the correct order before they are bound or stapled. Ink stains on fabric can be frustrating, but there are ways to remove them. For example, how to get ink stains out of fabric provides tips on removing ink stains from different types of fabric.
Returning to printing collate, it is important to ensure that the pages are collated correctly to create a professional-looking document.
Collation as an Art Form

Collation transcends its practical applications and enters the realm of art. In the hands of skilled artisans, it becomes a medium for expressing creativity and storytelling.
Collation in Bookbinding
Bookbinding is one of the most prominent art forms that utilizes collation. By carefully arranging and assembling printed sheets, bookbinders create visually stunning and structurally sound books. Collation allows for the creation of unique page sequences, customized layouts, and intricate binding patterns.
One notable example is the work of British artist Derek Jarman. His book, “The Garden,” features a series of hand-collated pages with handwritten text and botanical illustrations. The collation process became an integral part of the artwork, creating a tactile and visually engaging experience for readers.
Collation in Other Creative Projects
Beyond bookbinding, collation finds its way into various creative endeavors. Artists use it to construct collages, sculptures, and mixed-media installations. By juxtaposing and layering printed materials, they create thought-provoking and visually stimulating works.
For instance, American artist Kara Walker’s silhouette collages often incorporate collaged elements. Her work explores themes of race, gender, and history, and collation serves as a powerful tool for conveying these narratives.
Collation for Sustainability

Collation processes can have an environmental impact, primarily through the consumption of materials and energy. However, sustainable practices can be implemented to minimize this impact.
Sustainable Collation Practices
- Using Recycled Materials:Using recycled paper, cardboard, and other materials for collation reduces the demand for virgin resources and conserves natural habitats.
- Reducing Waste:Optimizing collation processes to minimize waste, such as using automated systems that reduce overproduction and spoilage, and implementing waste recycling programs.
- Energy Efficiency:Employing energy-efficient collation equipment, such as LED lighting and variable-speed drives, and optimizing production schedules to reduce energy consumption.
Tips for Minimizing Environmental Footprint
- Assess the environmental impact of current collation practices.
- Implement sustainable practices, such as those mentioned above.
- Educate employees and stakeholders about the importance of sustainability.
- Monitor and track progress to identify areas for further improvement.
Collation and Digital Printing
Collation in digital printing presents unique challenges and opportunities. Digital printing technologies impact the collation process by enabling faster, more efficient, and customized collation methods.
Challenges of Collation in Digital Printing
- Variable page counts:Digital printing allows for variable data printing, resulting in documents with varying page counts, making collation more complex.
- Short-run printing:Digital printing often involves shorter print runs, requiring more frequent collation tasks.
- Paper handling:Digital printing processes can use different paper types and sizes, which can affect collation accuracy.
Opportunities of Collation in Digital Printing
- Automation:Digital printing technologies enable automated collation processes, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
- Customization:Digital printing allows for variable data printing, enabling personalized collation based on recipient data.
- Cost-effectiveness:Automated collation processes can reduce labor costs and improve overall efficiency, leading to cost savings.
Innovative Collation Solutions for Digital Printing
- Inline collation systems:These systems integrate collation directly into the digital printing process, automating the alignment and stacking of pages.
- Off-line collation systems:These systems perform collation as a separate process after printing, allowing for greater flexibility in handling different document types.
- Hybrid collation systems:These systems combine inline and off-line collation methods, providing a balance of speed and flexibility.
Role of Automation in Streamlining Collation
- Automated collation systems reduce manual labor, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Automated systems can handle complex collation tasks, such as variable page counts and custom sorting.
- Automation enables real-time monitoring and control of the collation process, minimizing errors.
Impact of Digital Printing on the Cost and Efficiency of Collation, What does printing collate mean
- Automated collation systems reduce labor costs and improve overall efficiency, leading to cost savings.
- Digital printing allows for shorter print runs, reducing the need for large-scale collation operations.
- Variable data printing enables personalized collation, eliminating the need for manual sorting and assembly.
Use of Variable Data Printing for Personalized Collation
- Variable data printing allows for each printed document to have unique data, such as recipient name or address.
- Personalized collation based on variable data ensures that each document is collated in the correct order for the intended recipient.
- This eliminates the need for manual sorting and assembly, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations of Digital Collation Solutions
- Example 1:A large financial institution implemented an automated collation system to handle high-volume, variable-page-count documents. The system reduced collation time by 75% and improved accuracy by 99%.
- Example 2:A healthcare provider used a hybrid collation system to personalize patient records based on variable data. The system improved patient satisfaction and reduced turnaround time for record delivery.
Future Trends and Advancements in Digital Collation Technology
- Artificial intelligence (AI):AI algorithms can optimize collation processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Cloud-based collation services:Cloud-based platforms can provide remote access to collation services, enabling collaboration and scalability.
- Internet of Things (IoT):IoT devices can monitor and control collation equipment, providing real-time insights and predictive maintenance.
Table: Key Differences between Traditional and Digital Collation Methods
| Traditional Collation | Digital Collation |
|---|---|
| Manual, labor-intensive process | Automated, streamlined process |
| Limited customization options | Personalized collation based on variable data |
| Higher cost and longer turnaround time | Lower cost and faster turnaround time |
| Prone to errors | High accuracy and reliability |
Flowchart Illustrating the Typical Workflow of a Digital Collation Process
[Provide a flowchart illustrating the typical workflow of a digital collation process.]
Glossary of Terms Related to Collation in Digital Printing
- Collation:The process of gathering and assembling printed pages in the correct order.
- Inline collation:Collation performed during the printing process.
- Off-line collation:Collation performed as a separate process after printing.
- Variable data printing:Printing technology that allows for each printed document to have unique data.
- Automated collation system:A system that uses automation to perform collation tasks.
Collation in Packaging

Collation is a crucial process in packaging and shipping, as it ensures that products are grouped and organized efficiently for optimal packaging and transportation.
Collating products offers numerous benefits, including reduced packaging materials, increased shipping efficiency, and improved product protection. It allows for the consolidation of multiple items into a single package, minimizing the amount of packaging materials required and reducing overall packaging costs.
Collation Techniques in Packaging
- Hand Collation:Manual grouping of products, typically for small quantities or specialty items.
- Automated Collation:Using machines to group and assemble products, increasing speed and efficiency for large-scale operations.
- Semi-Automated Collation:Combining manual and automated processes, providing flexibility and cost-effectiveness.
Collation Equipment
- Collating Machines:Automated systems that gather and assemble products in a specific order.
- Collating Tables:Manual workstations with designated areas for each product, facilitating hand collation.
- Collating Conveyor Systems:Automated conveyors that transport and group products.
Choosing a Collation Method
- Volume:High-volume operations typically require automated or semi-automated collation.
- Product Type:Fragile or irregularly shaped products may require manual collation.
- Cost:Manual collation is typically less expensive for small-scale operations, while automated collation offers cost savings for large-scale operations.
- Space:Automated collation machines require dedicated space, while manual collation can be done in smaller areas.
Optimizing Collation Efficiency
- Product Standardization:Consistent product dimensions and packaging facilitate automated collation.
- Optimized Packaging:Designing packaging to accommodate specific collation methods improves efficiency.
- Training:Proper training of personnel ensures accurate and efficient manual collation.
- Maintenance:Regular maintenance of collation equipment minimizes downtime and ensures optimal performance.
Latest Trends and Innovations
- Advanced Automation:Robotic systems and artificial intelligence enhance speed and accuracy.
- Sustainable Collation:Biodegradable and recyclable materials reduce environmental impact.
- Data Integration:Collation systems integrated with inventory and order management systems improve efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainable Alternatives
- Minimizing Packaging Waste:Collation reduces the amount of packaging materials used.
- Biodegradable and Recyclable Materials:Using sustainable materials for collation minimizes environmental impact.
- Optimized Transportation:Efficient collation reduces the number of shipments, lowering carbon emissions.
Glossary of Terms
- Collation:The process of grouping and assembling products in a specific order.
- Collating Machine:An automated system used for collating products.
- Collating Table:A manual workstation used for collating products.
- Collating Conveyor System:An automated conveyor system used for collating products.
Case Study: Successful Collation Implementation
A manufacturing company implemented an automated collation system, resulting in a 30% reduction in packaging materials, a 20% increase in shipping efficiency, and a significant reduction in product damage during transit.
FAQ
What is the purpose of collating in printing?
Collating ensures that printed sheets are arranged in the correct order, making it easier to assemble and read the final document.
What are the different types of collating equipment?
Collating equipment ranges from manual tabletop models to automated high-volume systems, each with its own advantages and capabilities.
What factors should be considered when choosing a collating method?
Factors to consider include the volume of documents, the complexity of the collation order, and the desired level of automation.


