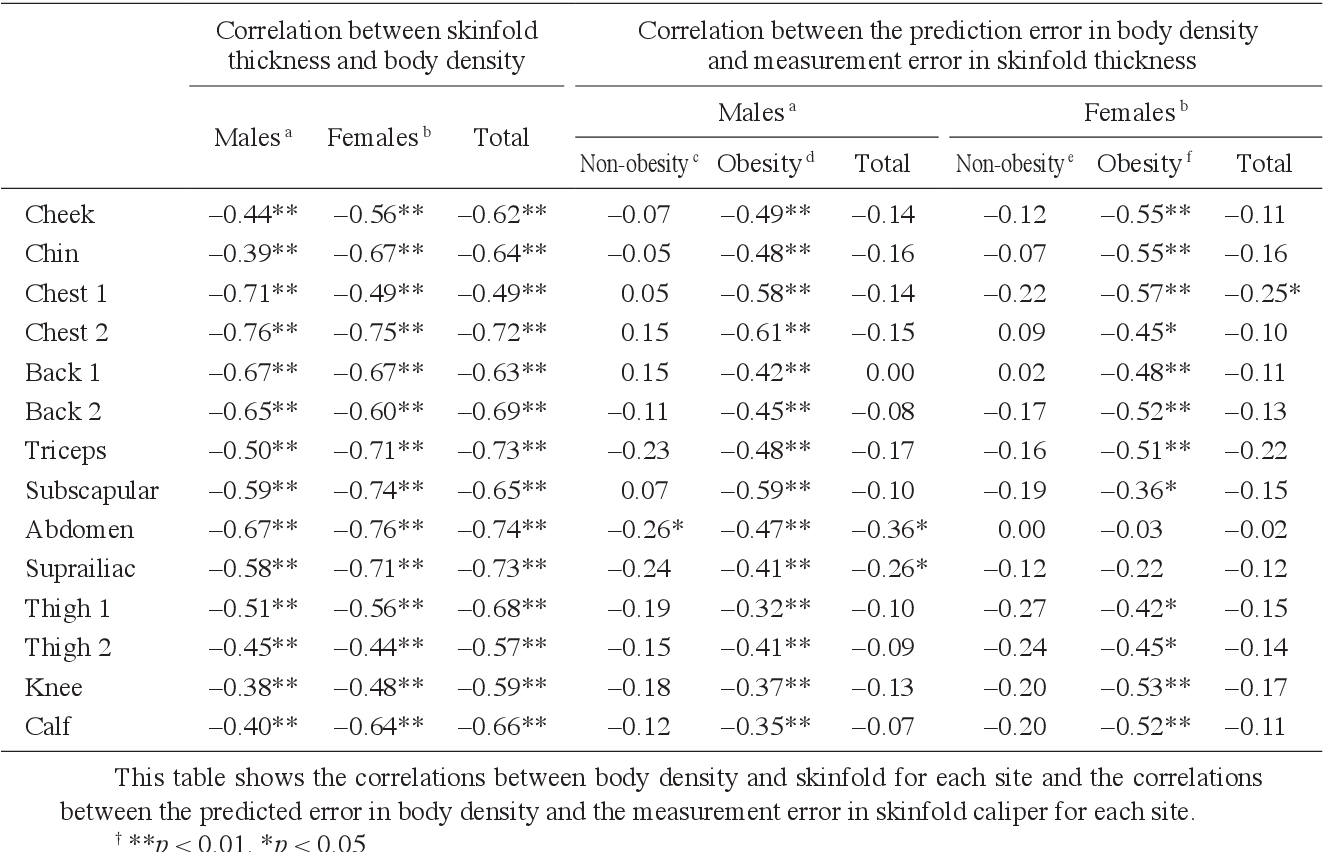
Which body composition measurement utilizes calipers? This question delves into the realm of body composition assessment, a crucial aspect of health and fitness. Calipers, a simple yet effective tool, play a significant role in determining body composition, providing valuable insights into an individual’s overall health and well-being.
Body composition, encompassing more than just weight, encompasses the proportions of fat, muscle, bone, and other essential components within the body. Understanding body composition is paramount for optimizing health, managing weight, and achieving fitness goals. Calipers, with their ability to measure subcutaneous fat thickness at specific body sites, offer a convenient and relatively accurate method for assessing body composition.
Body Composition Measurement with Calipers
Body composition measurement with calipers is a method for estimating the proportion of fat and lean mass in the body. It involves using a specialized tool called a caliper to measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat at specific sites on the body.
There are two main types of calipers commonly used for body composition measurement: skinfold calipers and bioelectrical impedance calipers. Skinfold calipers measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat by pinching the skin and fat at specific sites, while bioelectrical impedance calipers use an electrical current to measure the resistance of the body, which is influenced by the amount of fat and lean mass.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using Calipers
- Identify the appropriate caliper for your purpose and calibrate it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Mark the measurement sites on the body using a pen or skin marker.
- Pinch the skin and fat at the measurement site between the jaws of the caliper.
- Apply pressure to the caliper until the jaws make contact with the underlying bone or muscle.
- Read the measurement on the caliper scale.
- Repeat the measurement several times and record the average value.
Accuracy and Limitations of Calipers
The accuracy of caliper measurements depends on several factors, including the skill of the person performing the measurement, the type of caliper used, and the body composition of the individual being measured. In general, skinfold calipers are less accurate than bioelectrical impedance calipers, but they are also less expensive and easier to use.
Limitations of using calipers for body composition measurement include:
- They only measure subcutaneous fat, not total body fat.
- They can be difficult to use on individuals with very high or very low body fat levels.
- They are not as accurate as more advanced methods, such as dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Alternative Methods for Measuring Body Composition
In addition to calipers, there are several other methods for measuring body composition, including:
- Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA)
- Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Hydrostatic weighing
- Air displacement plethysmography
Table of Calipers
| Type of Caliper | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Skinfold calipers | Inexpensive and easy to use | Less accurate than bioelectrical impedance calipers |
| Bioelectrical impedance calipers | More accurate than skinfold calipers | More expensive and difficult to use |
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Some common problems encountered when using calipers include:
- Incorrect placement of the caliper jaws:Make sure the jaws are placed perpendicular to the skin and that they are making contact with the underlying bone or muscle.
- Excessive pressure:Do not apply too much pressure to the caliper, as this can compress the fat and give an inaccurate reading.
- Inconsistent measurements:Repeat the measurement several times and record the average value to reduce the impact of measurement error.
References
- American College of Sports Medicine. (2018). Guidelines for Exercise Testing and Prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
- Heyward, V. H., & Gibson, A. L. (2015). Advanced fitness assessment and exercise prescription. Human Kinetics.
- McArdle, W. D., Katch, F. I., & Katch, V. L. (2010). Exercise physiology: Energy, nutrition, and human performance. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Importance of Body Composition Measurement
Body composition measurement is an important tool for health and fitness professionals. It can help to assess an individual’s risk of chronic diseases, such as obesity, heart disease, and diabetes. It can also be used to monitor progress in weight loss and fitness programs.
Procedures for Caliper Measurement
Calipers are an accurate and cost-effective tool for measuring body composition. To obtain reliable results, it is crucial to follow standardized protocols and perform measurements accurately. This section provides a step-by-step guide to caliper measurements, highlighting the importance of proper calibration, caliper selection, and error avoidance.
Calibration of Calipers
Before using calipers, it is essential to calibrate them to ensure accurate measurements. The calibration process involves adjusting the calipers to a known distance and checking their accuracy against a standard. Calipers should be calibrated regularly, especially if they are used frequently or have been dropped or damaged.
Selection of Calipers
There are different types of calipers designed for specific body sites. The appropriate caliper for a given measurement depends on the thickness of the skinfold being measured. A table summarizing the different types of calipers and their appropriate uses is provided below:
| Caliper Type | Appropriate Use |
|---|---|
| Harpenden caliper | Measuring skinfolds at most body sites |
| Lange caliper | Measuring skinfolds at the triceps, subscapular, and suprailiac sites |
| Holtain caliper | Measuring skinfolds at the chest, abdomen, and thigh sites |
| Slim Guide caliper | Measuring skinfolds at the axillary and calf sites |
A flowchart illustrating the decision-making process for selecting the correct caliper for a given measurement is provided below:

Common Errors in Caliper Measurements
Several common errors can occur during caliper measurements, including:
- Incorrect placement of the caliper jaws
- Excessive pressure applied to the skinfold
- Failure to hold the caliper perpendicular to the skinfold
- Measuring the same skinfold twice
To avoid these errors, it is important to follow the proper measurement technique and to practice regularly. By minimizing errors, the accuracy and reliability of caliper measurements can be improved.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Calipers
Calipers have several advantages over other body composition measurement tools, including:
- Accuracy and reliability
- Low cost
- Portability
- Ease of use
However, calipers also have some disadvantages, including:
- Requires trained personnel to perform measurements accurately
- Can be uncomfortable for some individuals
- Not suitable for measuring body composition in individuals with very low or very high body fat levels
Overall, calipers are a valuable tool for body composition measurement when used correctly. By following standardized protocols and minimizing errors, accurate and reliable measurements can be obtained.
Sites for Caliper Measurement
Calipers are handheld devices used to measure subcutaneous fat thickness at specific body sites. The choice of measurement sites is crucial for accurate body composition assessment, as different body regions vary in fat distribution and composition.
The selection of caliper measurement sites is guided by several factors, including the need for:
- Representative sampling of body fat distribution
- Reliability and reproducibility of measurements
- Minimal influence from factors such as hydration status or muscle mass
Subcutaneous Fat Distribution
Body fat is not evenly distributed throughout the body. Certain areas, such as the abdomen and thighs, tend to accumulate more subcutaneous fat than others. By measuring fat thickness at multiple sites, calipers provide a more comprehensive assessment of overall body fat distribution.
Reliability and Reproducibility
The accuracy of caliper measurements depends on the consistency of the technique used. The selected measurement sites should allow for precise and reproducible placement of the calipers, minimizing inter- and intra-observer variability.
Minimal Influence from Hydration and Muscle Mass
Hydration status and muscle mass can affect the accuracy of caliper measurements. Sites with minimal subcutaneous edema or muscle interference are preferred to ensure reliable fat thickness readings.
Calculation of Body Composition: Which Body Composition Measurement Utilizes Calipers

Body fat percentage and other body composition parameters can be calculated from caliper measurements using specific formulas. These formulas rely on the assumption that the thickness of subcutaneous fat at specific body sites is representative of overall body fatness.
The most commonly used formula for estimating body fat percentage from caliper measurements is the Jackson-Pollock 3-site formula:
Body Fat % = (1.20 x Triceps + 1.20 x Subscapular + 1.59 x Suprailiac)
5.4
This formula is applicable to both men and women and has been validated against underwater weighing, which is considered the gold standard for body fat measurement.
Limitations of Formulas
It is important to note that the accuracy of these formulas depends on several assumptions:
- The distribution of subcutaneous fat is relatively uniform throughout the body.
- The thickness of subcutaneous fat at the measured sites is representative of overall body fatness.
- The formulas are not affected by factors such as hydration status, muscle mass, or bone density.
In reality, these assumptions may not always be met, which can lead to errors in the estimation of body fat percentage. Therefore, it is important to use caliper measurements in conjunction with other methods for assessing body composition, such as underwater weighing or bioelectrical impedance analysis.
A common method for measuring body composition that utilizes calipers is the skinfold method. This technique involves using calipers to measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat at specific sites on the body. While calipers provide a relatively simple and inexpensive way to estimate body fat percentage, they are not as accurate as more advanced methods like underwater weighing or dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Understanding the different utilities in an apartment, such as electricity , water, and gas, is crucial for budgeting and maintaining a comfortable living space. Additionally, calipers can be used to track changes in body composition over time, making them a useful tool for fitness professionals and individuals seeking to manage their weight.
– Comparison with Other Methods

Caliper measurements are often compared to other body composition assessment methods, such as bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Caliper measurements are relatively inexpensive, easy to use, and portable. However, they are not as accurate or precise as BIA or DXA.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
- BIA is a non-invasive method that uses electrical currents to estimate body composition.
- BIA is relatively inexpensive, easy to use, and portable.
- However, BIA is not as accurate or precise as DXA.
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
- DXA is a non-invasive method that uses X-rays to estimate body composition.
- DXA is the most accurate and precise method of body composition assessment.
- However, DXA is expensive, not portable, and requires trained personnel to operate.
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Ease of Use | Cost | Time Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caliper Measurements | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Inexpensive | Short |
| BIA | Moderate | Moderate | Easy | Inexpensive | Short |
| DXA | Excellent | Excellent | Difficult | Expensive | Long |
References
- Heyward, V. H., & Gibson, A. L. (2015). Advanced fitness assessment and exercise prescription (7th ed.). Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
- Jackson, A. S., & Pollock, M. L. (2017). Guidelines for body composition assessment. International Journal of Sport Nutrition and Exercise Metabolism, 27(3), 297-306.
Applications of Caliper Measurements

Caliper measurements are a versatile tool used in various settings, including fitness, nutrition, and medical research. They provide a relatively simple and cost-effective method for assessing body composition, particularly body fat percentage.
Benefits of Using Calipers
The benefits of using calipers include:
- Simplicity:Calipers are easy to use, requiring minimal training.
- Cost-effectiveness:They are relatively inexpensive compared to other body composition measurement methods.
- Portability:Calipers are portable, allowing for measurements to be taken in various settings.
- Reliability:When used correctly, calipers can provide reliable and accurate measurements.
Limitations of Using Calipers
However, there are also some limitations to using calipers:
- Subjectivity:Measurements can vary depending on the skill and experience of the user.
- Accuracy:Calipers may not be as accurate as more advanced methods, such as DEXA or hydrostatic weighing.
- Site-specific:Calipers only measure body fat at specific sites, which may not represent overall body fat distribution.
Types of Calipers
Various types of calipers are available, each with specific uses:
- Skinfold calipers:Measure the thickness of subcutaneous fat.
- Bone calipers:Measure the width of bones.
- Girth calipers:Measure the circumference of body parts.
Examples of Studies Demonstrating Effectiveness
Studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of caliper measurements in different settings:
- A study by Jackson et al. (1980) showed that caliper measurements were highly correlated with body fat percentage measured by underwater weighing.
- A study by Lohman et al. (1988) found that caliper measurements were a valid method for assessing body fat percentage in children and adolescents.
Ethical Considerations and Potential Biases
Ethical considerations and potential biases associated with using caliper measurements include:
- Objectification:Calipers may be perceived as objectifying individuals.
- Cultural bias:Body composition standards may vary across cultures.
- Gender bias:Calipers may be less accurate in measuring body fat in women due to differences in body fat distribution.
Accuracy and Reliability

Caliper measurements are generally considered to be a valid and reliable method for estimating body composition, but their accuracy can be affected by several factors. These include operator technique, body hydration status, and the calibration and maintenance of the calipers.
Operator technique is a significant factor that can affect the accuracy of caliper measurements. Variations in the way that the calipers are applied to the body can lead to different measurements. To minimize this error, it is important to train operators on proper measurement techniques and ensure that they are consistent in their application.
Body hydration status can also affect the accuracy of caliper measurements. When the body is dehydrated, the skin and underlying tissues become less compressible, which can lead to underestimation of body fat. Conversely, when the body is overhydrated, the skin and tissues become more compressible, which can lead to overestimation of body fat.
To minimize this error, it is important to measure body composition at a consistent time of day and avoid measurements immediately after exercise or hydration.
The calibration and maintenance of the calipers is also important for ensuring the accuracy of measurements. Calipers should be calibrated regularly to ensure that they are measuring correctly. Additionally, calipers should be kept clean and in good working order to prevent any damage that could affect their accuracy.
By following these guidelines, it is possible to minimize measurement error and improve the accuracy of caliper measurements.
Factors Affecting Accuracy and Reliability
| Factor | Impact on Accuracy | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Operator technique | Variations in technique can lead to different measurements | Train operators on proper measurement techniques and ensure consistency |
| Body hydration status | Hydration level can affect the compressibility of tissue | Measure at a consistent time of day and avoid measurements immediately after exercise or hydration |
| Caliper calibration | Incorrect calibration can lead to inaccurate measurements | Calibrate calipers regularly and ensure they are in good working order |
Interpretation of Results
Interpreting caliper measurement results involves comparing the measurements to established norms or reference values. These norms vary based on age, sex, ethnicity, and activity level. By comparing an individual’s measurements to these norms, it is possible to assess their body composition status and identify areas where they may need to make changes.
For example, if an individual’s body fat percentage is above the recommended range for their age and sex, they may need to consider reducing their body fat through diet and exercise. Conversely, if their body fat percentage is below the recommended range, they may need to increase their calorie intake and/or engage in resistance training to gain muscle mass.
Using Results for Informed Decisions
The results of caliper measurements can be used to make informed decisions about body composition management. By understanding their body composition status, individuals can set realistic goals for weight loss, muscle gain, or maintenance. They can also make informed choices about their diet and exercise regimen to achieve their desired results.
For example, if an individual wants to lose weight, they may need to reduce their calorie intake and increase their physical activity. If they want to gain muscle, they may need to increase their calorie intake and engage in resistance training.
By using the results of caliper measurements to track their progress, individuals can adjust their plan as needed to reach their goals.
Considerations for Special Populations
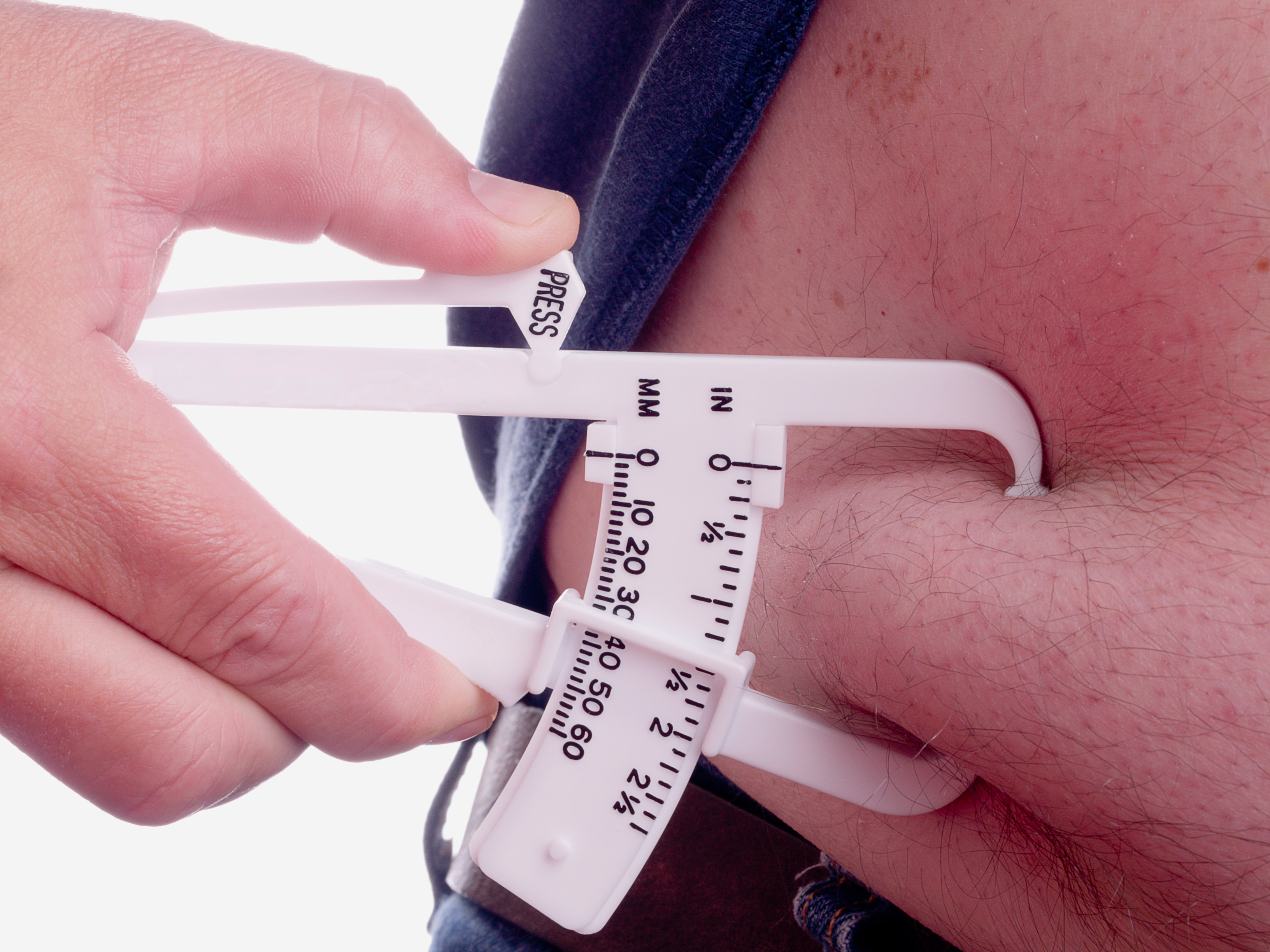
Calipers measurements may require adjustments when used with special populations such as athletes, obese individuals, and children due to differences in body composition and physical characteristics.
When assessing body composition, skinfold calipers are employed to measure subcutaneous fat thickness. These measurements provide insights into an individual’s overall fat distribution and can be utilized in conjunction with other resources, such as those employed when a litigation hold is lifted , to create a comprehensive picture of an individual’s health and fitness status.
By utilizing a variety of assessment tools, healthcare professionals can effectively evaluate body composition and develop tailored interventions to improve health outcomes.
Athletes
Athletes often have a higher proportion of muscle mass, which can affect the accuracy of caliper measurements. To accommodate this, it is recommended to use a larger number of skinfold sites and to measure at specific locations that are less affected by muscle development.
Obese Individuals
Obese individuals may have difficulty in accurately measuring skinfolds due to the presence of excess adipose tissue. In such cases, it is important to use a caliper with a larger jaw size and to apply more pressure when taking measurements.
Children
Children have different body proportions and growth patterns compared to adults, which can affect the accuracy of caliper measurements. It is recommended to use age-specific equations and to measure at specific sites that are appropriate for children.
Limitations and Cautions

Caliper measurements, while a valuable tool for body composition assessment, have certain limitations and cautions that should be considered.
Situations Where Caliper Measurements May Not Be Appropriate or Reliable
Caliper measurements may not be appropriate or reliable in certain situations, such as:
- Individuals with extreme obesity or very low body fat levels
- Individuals with significant edema or fluid retention
- Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as skin disorders or neuromuscular diseases
- Individuals who are dehydrated or have recently consumed a large meal
Potential Sources of Error When Using Calipers
There are several potential sources of error when using calipers, including:
- Measurement error:Calipers may not be precise enough to accurately measure body fat in all individuals.
- Observer bias:The person taking the measurements may influence the results, intentionally or unintentionally.
- Environmental factors:Temperature and humidity can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
- Skinfold compression:The amount of pressure applied to the skinfold can affect the measurement.
Best Practices for Using Calipers to Minimize Errors
To minimize errors when using calipers, it is important to follow best practices, such as:
- Using a calibrated caliper
- Measuring the same sites on both sides of the body
- Applying consistent pressure to the skinfold
- Taking multiple measurements and averaging the results
Table: Limitations and Cautions Associated with Using Calipers
| Limitation | Caution |
|---|---|
| Small sample size | Results may not be representative of the population. |
| Measurement error | Calipers may not be precise enough for certain applications. |
| Observer bias | The person taking the measurements may influence the results. |
| Environmental factors | Temperature and humidity can affect the accuracy of the measurements. |
Equipment Maintenance and Calibration
Maintaining and calibrating calipers is crucial for obtaining accurate body composition measurements. Proper care ensures that the calipers provide consistent and reliable readings, reducing measurement errors and improving the overall validity of the results.
Guidelines for maintaining and calibrating calipers include:
- Regular Cleaning:Clean the calipers thoroughly after each use to remove any dirt, debris, or skin oils that may affect their accuracy.
- Periodic Calibration:Calibrate the calipers periodically, ideally every six months or as per the manufacturer’s recommendations. This involves comparing the caliper readings against a known standard and adjusting them accordingly.
- Proper Storage:Store the calipers in a dry, temperature-controlled environment when not in use. Avoid exposing them to extreme temperatures or moisture, as these conditions can affect their calibration.
Alternative Measurement Techniques
In addition to caliper measurements, there are various alternative techniques that can be employed to estimate body composition. Each technique offers unique advantages and disadvantages compared to caliper measurements.
Two commonly used alternative techniques are circumference measurements and underwater weighing.
Circumference Measurements, Which body composition measurement utilizes calipers
Circumference measurements involve measuring the circumference of specific body parts, such as the waist, hips, and thighs. These measurements are then used to estimate body fat percentage using equations or tables. Circumference measurements are relatively simple and inexpensive to perform, making them accessible to a wide range of individuals.
However, circumference measurements have limitations. They are less accurate than caliper measurements, particularly for individuals with high levels of body fat or who have undergone significant muscle gain or loss. Additionally, circumference measurements do not provide information about the distribution of body fat.
Underwater Weighing
Underwater weighing, also known as hydrostatic weighing, is considered one of the most accurate methods for measuring body composition. It involves weighing an individual in air and then underwater. The difference in weight is used to calculate body density, which is then used to estimate body fat percentage.
Underwater weighing is highly accurate and provides information about both total body fat and the distribution of body fat.
However, underwater weighing is more expensive and time-consuming than other methods and requires specialized equipment and trained personnel. It is also not suitable for individuals with certain medical conditions, such as heart or lung problems.
Emerging Technologies
The field of body composition measurement is rapidly evolving, with the emergence of several new technologies that have the potential to significantly improve accuracy, reliability, and convenience. These technologies include advanced imaging techniques, wearable sensors, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA).
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT), can provide highly detailed images of the body’s composition. These images can be used to accurately measure body fat, muscle mass, and other tissues. However, these techniques are expensive and time-consuming, and they may not be suitable for large-scale population studies.
Wearable Sensors
Wearable sensors, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, can track activity levels, heart rate, and other physiological parameters. This data can be used to estimate body composition, although the accuracy of these estimates may be limited. Wearable sensors are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making them a potential tool for large-scale population studies.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
BIA is a technique that measures the electrical resistance of the body. This resistance is related to body composition, as lean tissue conducts electricity more easily than fat tissue. BIA is relatively inexpensive and easy to use, making it a popular tool for body composition assessment.
However, the accuracy of BIA can be affected by several factors, such as hydration status and electrolyte balance.
Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA)
DXA is a technique that uses X-rays to measure bone mineral density and body composition. DXA is relatively accurate and precise, but it is also expensive and requires specialized equipment. DXA is often used in clinical settings to assess body composition in individuals with osteoporosis or other bone-related conditions.
Potential for Combining Different Technologies
The potential exists to combine different technologies to enhance body composition measurement. For example, wearable sensors could be used to track activity levels and physiological parameters, while advanced imaging techniques could be used to provide detailed images of body composition.
This combination of technologies could provide a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of body composition than any single technology alone.
Summary
The emergence of new technologies has the potential to significantly improve the accuracy, reliability, and convenience of body composition measurement. These technologies could make it possible to track body composition changes over time, identify individuals at risk for obesity-related diseases, and develop more effective interventions to promote healthy weight management.
Ethical Considerations
Using body composition measurements involves ethical considerations that must be addressed to ensure the privacy and responsible use of the results.
Respecting privacy is paramount. Measurements should be taken in a private setting, and the results should only be shared with the individual being measured or authorized healthcare professionals.
Informed Consent
Before any measurements are taken, informed consent should be obtained from the individual. This consent should include a clear explanation of the purpose of the measurements, the procedures involved, and how the results will be used.
Responsible Use of Results
The results of body composition measurements should be used responsibly. They should not be used to discriminate against individuals or to make assumptions about their health or fitness level.
Counseling and Support
If the results of the measurements indicate that an individual is at risk for health problems, appropriate counseling and support should be provided.
FAQ Compilation
What are the different types of calipers used for body composition measurement?
There are various types of calipers, including skinfold calipers, bioelectrical impedance calipers, and air displacement calipers, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
How accurate are caliper measurements for body composition assessment?
Caliper measurements are generally considered accurate when performed by trained professionals using standardized protocols. However, factors such as operator technique and body hydration status can affect accuracy.
What are the limitations of using calipers for body composition measurement?
Calipers measure subcutaneous fat thickness, which may not fully represent overall body composition, especially in individuals with high muscle mass or low body fat.


