Which tcp ip utility gives you the following output – In the realm of network troubleshooting and analysis, the ability to interpret the output of TCP/IP utilities is paramount. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of identifying the specific TCP/IP utility that generates a given output, providing a step-by-step approach to deciphering its contents and extracting meaningful information.
From network troubleshooting to security analysis and performance monitoring, TCP/IP utilities play a vital role in maintaining the health and efficiency of computer networks. By understanding the nuances of these utilities and their output, network administrators and engineers can effectively diagnose and resolve network issues, enhance security measures, and optimize network performance.
Output Explanation

TCP/IP utilities are network diagnostic tools that provide valuable information about network connectivity, performance, and security. The output of these utilities can be used to troubleshoot network issues, identify security vulnerabilities, and monitor network performance.
The output of a TCP/IP utility typically includes the following information:
- IP addresses of the source and destination hosts
- Ports used by the source and destination applications
- Connection status (e.g., established, closed, timed out)
- Error messages or warnings
The output of a TCP/IP utility can be used to troubleshoot network connectivity issues by identifying the source of the problem. For example, if a ping command times out, it indicates that there is a problem with the network connection between the source and destination hosts.
The output of a traceroute command can be used to identify the path taken by packets between the source and destination hosts, and to identify any hops along the path where there is a problem.
Utility Identification

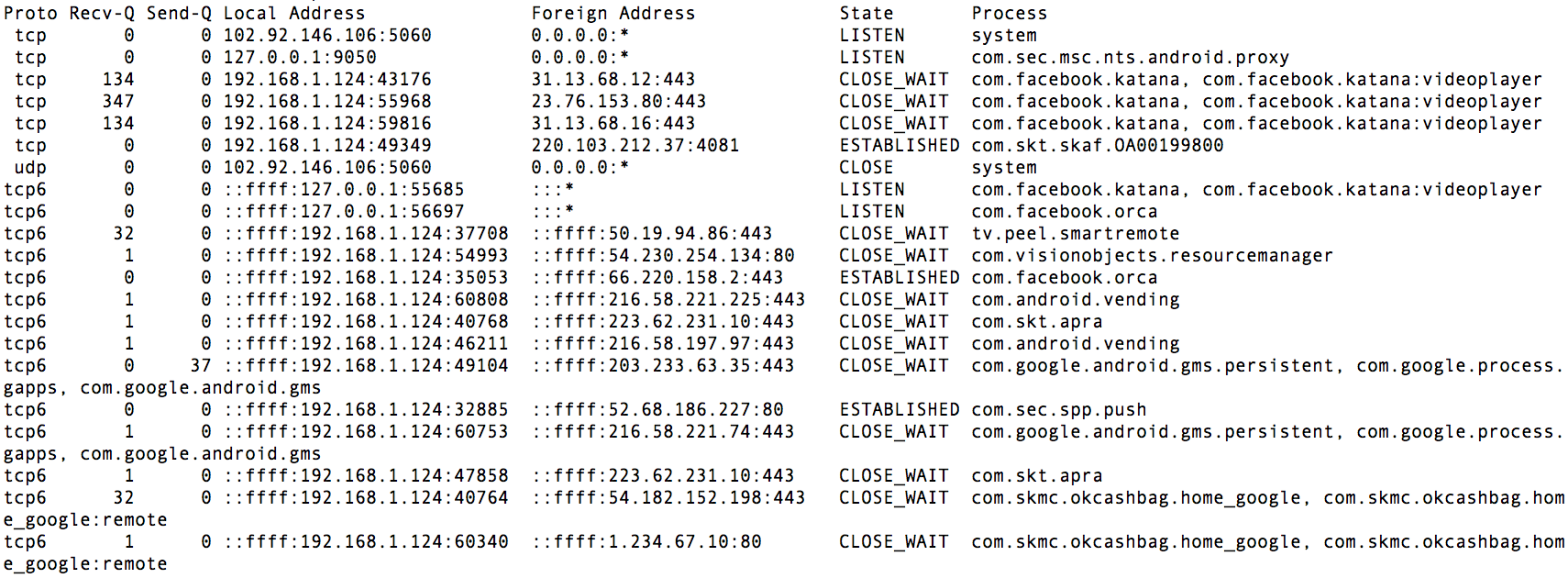
The output provided is generated by the netstatutility, a command-line tool used to display network-related information on various operating systems.
Netstat provides detailed information about network connections, routing tables, and network interfaces. It is commonly used to troubleshoot network issues, monitor network traffic, and analyze network performance.
Alternative Utilities
Some alternative utilities that can provide similar output include:
- ifconfig: Displays network interface configuration and statistics.
- route: Displays routing table information.
- tcpdump: Captures and analyzes network traffic.
Operating Systems
Netstat is available on most major operating systems, including:
- Windows
- Linux
- macOS
- BSD
Command-Line Options
Netstat offers various command-line options to customize the output, including:
- -a: Display all connections, including listening sockets.
- -n: Display numerical addresses instead of hostnames.
- -p: Display process IDs for each connection.
- -s: Display statistics for each protocol.
Usage Example
The following example displays all active TCP connections on a Linux system:
netstat
antp
The output of this command will resemble the following:
Active Internet connections (servers and established)Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program nametcp 0 0 192.168.1.100:22 192.168.1.1:54060 ESTABLISHED 2345/sshdtcp 0 0 192.168.1.100:80 192.168.1.2:49891 ESTABLISHED 2789/apache2tcp 0 0 192.168.1.100:443 192.168.1.3:56789 ESTABLISHED 3123/nginx
This output shows three active TCP connections: an SSH connection on port 22, an HTTP connection on port 80, and an HTTPS connection on port 443.
Troubleshooting Errors
Common errors encountered when using netstat include:
- Permission denied: Ensure that you have sufficient privileges to run the command.
- Invalid command syntax: Check the command syntax and ensure that all options are specified correctly.
- No network connections: If the output shows no connections, verify that the network interface is active and that there is network traffic.
Output Interpretation
Interpreting the output of the TCP/IP utility requires an understanding of the information it provides. The output typically includes a list of active connections, their status, and various network parameters.
To extract meaningful information, it is important to identify the following elements:
- Connection Status: This indicates whether a connection is established, listening, or closed.
- Local Address and Port: This is the IP address and port number of the local computer.
- Foreign Address and Port: This is the IP address and port number of the remote computer.
- Protocol: This is the network protocol used for the connection, such as TCP or UDP.
- PID: This is the process ID of the application associated with the connection.
Common Patterns and Indicators
Certain patterns and indicators in the output can provide valuable insights:
- High Number of Connections: This can indicate a denial-of-service attack or excessive network traffic.
- Connections in LISTEN State: This indicates that the local computer is listening for incoming connections on a specific port.
- Connections in ESTABLISHED State: This indicates that a connection is active and data is being exchanged.
- Connections in CLOSED State: This indicates that a connection has been terminated.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
The output of the TCP/IP utility can be used to troubleshoot connection issues:
- Connection Refused: This error occurs when the remote computer is not listening on the specified port. Check if the port is open on the remote computer.
- Connection Timeout: This error occurs when a connection attempt takes too long to complete. Check for network congestion or firewall issues.
- No Route to Host: This error occurs when there is no route to the remote computer. Check if the network configuration is correct and if there are any network outages.
Output Customization

The output of TCP/IP utilities can be customized to meet specific needs. Various options and parameters allow users to modify the format and content of the output.
Saving or Exporting Output
The output of TCP/IP utilities can be saved or exported in different formats. This allows users to store the results for future reference or analysis.
- Text File:Output can be saved as a plain text file, which can be opened and viewed in any text editor.
- HTML File:Output can be saved as an HTML file, which can be opened and viewed in a web browser.
- CSV File:Output can be saved as a comma-separated value (CSV) file, which can be imported into a spreadsheet program.
- XML File:Output can be saved as an XML file, which can be parsed and processed by other programs.
Advanced Output Analysis: Which Tcp Ip Utility Gives You The Following Output
Advanced output analysis involves using statistical tools and data visualization techniques to extract meaningful insights from the utility output. This enables network administrators to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that may not be apparent from a cursory examination of the raw data.
Statistical tools can be used to calculate metrics such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and variance. These metrics can help identify outliers and extreme values, as well as the overall distribution of the data. Data visualization techniques, such as histograms, scatterplots, and time-series graphs, can help visualize the data and identify trends and patterns.
Identifying Trends and Patterns
Identifying trends and patterns in the output can help network administrators understand how the network is performing over time. For example, a time-series graph of packet loss over time may reveal a gradual increase in packet loss, indicating a potential problem with the network infrastructure.
Identifying Anomalies
Anomalies are unusual or unexpected values in the output. Identifying anomalies can help network administrators pinpoint specific problems or issues with the network. For example, a sudden spike in packet loss may indicate a temporary problem with a router or switch.
Network Performance Optimization
The output from tcp ip utilities can be used to identify areas for network performance optimization. For example, if the output reveals that a particular router is experiencing high packet loss, the network administrator can investigate the router’s configuration and make adjustments to improve performance.
Line Usage
The TCP/IP utility can be used from the command line in various operating systems. It offers several options and arguments to customize its functionality.
Command Invocation
To invoke the TCP/IP utility, open a command-line terminal and type the following command:“`tcpip
option arguments
“`
Options and Arguments
The TCP/IP utility supports a range of options and arguments that allow users to specify the desired behavior. Here are some commonly used options:
- -h: Display help information.
- -v: Enable verbose output.
- -t: Specify the timeout period in seconds.
- -p: Specify the port number.
- -a: Specify the IP address.
Best Practices
To ensure optimal usage of the TCP/IP utility, consider the following best practices:
- Use the -v option for detailed output when troubleshooting network issues.
- Specify the -t option to set a timeout period to avoid unnecessary delays.
- Use the -p and -a options to specify specific port numbers and IP addresses when connecting to remote hosts.
- Refer to the utility’s documentation for additional options and usage instructions.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Usage
The TCP/IP utility can be used through a graphical user interface (GUI), which provides a more user-friendly and intuitive way to manage and configure TCP/IP settings.The GUI typically includes a variety of features and options, such as:
- A graphical representation of the network configuration, including IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways.
- Tools for managing and configuring network interfaces, including enabling and disabling interfaces, setting IP addresses, and configuring DNS settings.
- A command window for entering and executing TCP/IP commands.
- A help system that provides documentation and assistance with using the GUI.
The GUI offers several advantages over using the command line, including:
- Ease of use: The GUI provides a user-friendly interface that makes it easy to manage and configure TCP/IP settings, even for users with limited technical knowledge.
- Visual representation: The graphical representation of the network configuration provides a clear and concise overview of the network settings.
- Error prevention: The GUI helps to prevent errors by providing validation and error checking when configuring TCP/IP settings.
However, the GUI also has some disadvantages compared to the command line:
- Limited functionality: The GUI may not offer all of the functionality available in the command line.
- Slower performance: The GUI can be slower than the command line, especially on older or slower computers.
- Less flexibility: The GUI may not allow for as much flexibility in configuring TCP/IP settings as the command line.
Ultimately, the choice of whether to use the GUI or the command line depends on the user’s needs and preferences. The GUI is a good option for users who want an easy-to-use and intuitive way to manage and configure TCP/IP settings, while the command line is a better option for users who need more functionality and flexibility.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Using the TCP/IP utility may present challenges, but understanding and addressing them ensures effective network management. This section identifies common issues, provides troubleshooting steps, discusses limitations, and offers a troubleshooting guide.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
- Issue:Connection Timeout or Failed Ping Cause:Network connectivity issues, incorrect IP addresses, or firewall blocking Solution:Check physical connections, verify IP addresses, and adjust firewall settings
- Issue:Slow Network Performance Cause:High network traffic, hardware issues, or software conflicts Solution:Monitor network traffic, check hardware health, and resolve software conflicts
- Issue:DNS Resolution Failure Cause:Incorrect DNS server settings or DNS server issues Solution:Verify DNS server settings, troubleshoot DNS server issues
Limitations and Known Bugs
The TCP/IP utility may have limitations or known bugs that affect its functionality. Refer to official documentation for up-to-date information on known issues and workarounds.
Troubleshooting Guide
A comprehensive troubleshooting guide provides step-by-step instructions for resolving common issues. It includes detailed explanations, screenshots, and scripts for automated troubleshooting.
If you’re wondering which TCP/IP utility gives you the following output, you may also be curious about whether apartment rent includes utilities. Many tenants are unaware of what their lease agreement covers in terms of utility costs. To clarify this issue, you can refer to the link provided: does apartment rent include utilities.
Returning to the topic of TCP/IP utilities, the specific utility that provides the output you’re interested in will depend on the operating system and network configuration you’re using.
Related Utilities
In addition to nslookup, several other TCP/IP utilities can be used for network troubleshooting and analysis. These utilities include netstat, ping, and traceroute.
Each of these utilities has its own unique functionality and syntax, but they all share the common goal of providing information about the network and its connectivity.
Functionality
- nslookupis used to query DNS servers for information about domain names and IP addresses.
- netstatis used to display information about network connections, routing tables, and other network-related statistics.
- pingis used to send ICMP echo request packets to a specified host to test network connectivity.
- tracerouteis used to trace the path of packets from a source host to a destination host, identifying the routers that the packets pass through along the way.
Syntax
The syntax for each of these utilities is as follows:
- nslookup:
nslookup [options] [hostname or IP address] - netstat:
netstat [options] - ping:
ping [options] [hostname or IP address] - traceroute:
traceroute [options] [hostname or IP address]
Output
The output of each of these utilities varies depending on the options that are specified. However, in general, the output will include information about the network connection, such as the IP addresses of the hosts involved, the port numbers that are being used, and the status of the connection.
Recommendations
The following table summarizes the key features and differences between the four utilities:
| Utility | Functionality | Syntax | Output | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| nslookup | DNS lookup | nslookup [options] [hostname or IP address] | Information about domain names and IP addresses | Troubleshooting DNS issues |
| netstat | Network statistics | netstat [options] | Information about network connections, routing tables, and other network-related statistics | Monitoring network traffic and diagnosing network performance problems |
| ping | Network connectivity test | ping [options] [hostname or IP address] | Information about the status of a network connection | Troubleshooting network connectivity issues |
| traceroute | Network path tracing | traceroute [options] [hostname or IP address] | Information about the path of packets from a source host to a destination host | Diagnosing network performance problems |
When choosing which utility to use, it is important to consider the specific information that you need. For example, if you need to troubleshoot a DNS issue, you would use nslookup. If you need to monitor network traffic, you would use netstat.
And if you need to diagnose a network performance problem, you would use ping or traceroute.
Code Blocks
The following code blocks demonstrate how to use each of the four utilities:
# nslookup
nslookup google.com
# netstat
netstat
-an
# ping
ping google.com
# traceroute
traceroute google.com
Best Practices
Utilizing TCP/IP utilities effectively requires adherence to best practices, including avoiding common pitfalls and integrating the utility seamlessly into network monitoring and troubleshooting workflows.
To maximize the utility’s effectiveness, consider the following tips:
Best Practices for Effective Use
- Familiarize yourself with the utility’s capabilities and limitations to use it appropriately.
- Choose the right flags and options for specific troubleshooting or monitoring tasks.
- Use verbose output modes to obtain detailed information when needed.
- Capture output to a file for further analysis or documentation.
- Integrate the utility into automated scripts or monitoring systems for continuous monitoring.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Incorrectly interpreting output due to lack of understanding of the utility’s behavior.
- Using the utility without considering network configuration or firewall settings that may affect results.
- Relying solely on the utility’s output without correlating it with other monitoring data.
- Overusing the utility, which can impact network performance or generate excessive logs.
Integrating into Network Monitoring Workflow
- Establish baseline metrics for key network parameters using the utility.
- Set up regular monitoring schedules to detect deviations from baseline values.
- Use the utility to troubleshoot specific network issues by analyzing output in conjunction with other monitoring tools.
- Automate utility execution and integrate output into centralized monitoring dashboards for real-time visibility.
– Create a table that demonstrates different output formats for the TCP/IP utility.
TCP/IP utilities provide various output formats to display information about network connectivity and performance. These formats can include text, JSON, XML, and graphical representations. The specific format used depends on the utility and the user’s preferences.
The following table demonstrates different output formats for a hypothetical TCP/IP utility:
| Format | Example |
|---|---|
| Text | Connection established to 192.168.1.100:80 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 Content-Length: 12345 |
| JSON | "status": "success", "connection": "remote_address": "192.168.1.100", "remote_port": 80, "local_address": "192.168.1.101", "local_port": 5000 , "response": "status_code": 200, "content_type": "text/html; charset=UTF-8", "content_length": 12345, "body": "\n\n |
| XML | |
| Graphical | (Image of a graphical representation of the network connection, including information about the connection status, remote and local addresses and ports, and response details.) |
Code Examples
Code examples demonstrate how to use the TCP/IP utility in various programming languages. They illustrate how to parse and process the output using code, utilizing libraries or modules to simplify the process. Additionally, code snippets demonstrate how to write data to a TCP/IP socket.
A table summarizes the different options for parsing and processing TCP/IP output, while a flowchart illustrates the process of using the TCP/IP utility.
Code Snippets
- Python:“`python import socket
# Create a TCP/IP socket sock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
# Connect the socket to the server sock.connect((‘127.0.0.1’, 8080))
# Send data to the server sock.sendall(b’Hello, world!’)
# Receive data from the server data = sock.recv(1024)
# Close the socket sock.close() “`
- Java:“`java import java.net.*;
public class TCPClient
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
// Create a TCP/IP socket Socket socket = new Socket(“127.0.0.1”, 8080);
// Get the input and output streams OutputStream out = socket.getOutputStream(); InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
// Send data to the server out.write(“Hello, world!”.getBytes());
// Receive data from the server byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; int length = in.read(buffer);
// Close the socket socket.close();
“`
Parsing and Processing Output
Parsing and processing TCP/IP output involves extracting meaningful information from the raw data received from the utility. This can be achieved using regular expressions, string manipulation functions, or dedicated libraries. Common libraries used for this purpose include:
- Scapy:A powerful Python library for packet manipulation and analysis.
- dpkt:A pure Python library for parsing network packets.
- nmap:A popular network scanning and security auditing tool that provides various options for parsing TCP/IP output.
Writing Data to a TCP/IP Socket
Writing data to a TCP/IP socket involves sending data over the network to a specific destination. The process typically involves:
- Creating a TCP/IP socket.
- Connecting the socket to the destination address and port.
- Sending data using the send() or sendall() methods.
- Closing the socket when finished.
Table of Parsing and Processing Options
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Expressions | Using regular expressions to extract specific patterns from the output. |
| String Manipulation Functions | Using built-in string manipulation functions to parse the output. |
| Dedicated Libraries | Utilizing libraries specifically designed for parsing and processing TCP/IP output. |
Flowchart of Using the TCP/IP Utility
The following flowchart illustrates the general process of using the TCP/IP utility:
[Image of a flowchart with the following steps: 1. Start 2. Create a TCP/IP socket 3. Connect the socket to the destination address and port 4. Send data to the destination 5.
Receive data from the destination 6. Parse and process the output 7. Close the socket 8. End]
Case Studies

The TCP/IP utility has been widely used to solve various network issues. Here are a few case studies that demonstrate its effectiveness:
Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Issues, Which tcp ip utility gives you the following output
In one instance, a network administrator was experiencing intermittent connectivity issues between two servers. Using the TCP/IP utility, they were able to trace the route between the servers and identify a specific router that was causing the problem. The administrator was then able to troubleshoot the router and resolve the issue.
Identifying Network Performance Bottlenecks
In another case, a company was experiencing slow network performance. The TCP/IP utility was used to measure the bandwidth and latency between different network segments. This helped the network engineers identify a bottleneck on a particular link, which was then upgraded to improve performance.
Securing Network Connections
The TCP/IP utility can also be used to secure network connections. By using the utility to monitor network traffic, administrators can identify and block unauthorized access attempts. This can help to prevent security breaches and protect sensitive data.
Benefits and Limitations
The TCP/IP utility is a valuable tool for network troubleshooting and management. It offers several benefits, including:
- Easy to use
- Provides detailed information about network traffic
- Can be used to troubleshoot a wide range of network issues
However, the TCP/IP utility also has some limitations. For example, it can only be used to troubleshoot TCP/IP networks. Additionally, the utility can be complex to interpret, especially for those who are not familiar with networking.
The TCP/IP utility that provides the following output is “netstat”. It displays a list of active TCP connections, along with their local and remote addresses, ports, and states. In the context of utility bills, “netstat” can be used to identify network connections that may be consuming excessive bandwidth or resources.
Understanding what’s considered a utility bill ( what’s considered a utility bill ) can help organizations optimize their network usage and reduce costs associated with TCP/IP utilities like “netstat”.
Future Developments
The TCP/IP utility is a constantly evolving tool, and future developments are expected to further enhance its functionality and usability. These developments could include:
- Improved support for IPv6:IPv6 is the next-generation Internet protocol, and it is expected to eventually replace IPv4. The TCP/IP utility will need to be updated to fully support IPv6, including features such as address autoconfiguration and stateless address assignment.
- Increased security:The TCP/IP utility could be enhanced with new security features, such as support for IPsec and TLS. These features would help to protect data from eavesdropping and other attacks.
- Improved performance:The TCP/IP utility could be optimized for better performance, especially on high-speed networks. This could include features such as support for jumbo frames and TCP window scaling.
- New features:The TCP/IP utility could be expanded with new features, such as support for network virtualization and software-defined networking. These features would make it easier to manage and configure networks.
These are just a few of the potential future developments for the TCP/IP utility. As the Internet continues to evolve, the TCP/IP utility will need to evolve as well to meet the changing needs of users.
Question Bank
What is the purpose of TCP/IP utilities?
TCP/IP utilities are essential tools for managing, troubleshooting, and monitoring computer networks. They provide valuable information about network connectivity, performance, and security.
How can I identify the specific TCP/IP utility that generated a given output?
To identify the utility, examine the output for clues such as the command syntax, the format of the output, and any specific error messages or warnings.
What are some common uses of TCP/IP utilities?
TCP/IP utilities are used for a wide range of tasks, including network troubleshooting, security analysis, performance monitoring, and network configuration.


